Correlation between expression of p53, p21/WAF1, and MDM2 proteins and their prognostic significance in primary hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 20025780
- PMCID: PMC2809055
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-7-110
Correlation between expression of p53, p21/WAF1, and MDM2 proteins and their prognostic significance in primary hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Tumor Protein p53 (p53), cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21/WAF1), and murine double minute 2 (MDM2) participate in the regulation of cell growth. Altered expression of these gene products has been found in malignant tumors and has been associated with poor prognosis. Our aim was to investigate the expression of the 3 proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and their prognostic significance.
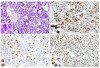
Methods: We examined p53, p21/WAF1, and MDM2 expression in 181 pairs of HCC tissues and the adjacent hepatic tissues by performing immunohistochemistry and examined the expression of the 3 proteins in 7 pairs of HCC tissues and the adjacent hepatic tissues by using western blot analysis.
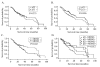
Results: The expression of p53, p21/WAF1, and MDM2 in the HCC tissues was significantly higher than those in the adjacent hepatic tissues (P < 0.05). A statistical correlation was observed between p53 and p21/WAF1 expression in HCC tissues (R = 0.195, P = 0.008). A statistical correlation was observed between expression of p53 and p21/WAF1 (R = 0.380, P = 0.000), p53 and MDM2 (R = 0.299, P = 0.000), p21/WAF1 and MDM2 (R = 0.285, P = 0.000) in 181 liver tissues adjacent to the tumor. Patients with a low pathologic grade HCC (I+II) had a higher tendency to express p53 on tumor cells than the patients with high pathologic grade HCC (III+IV) (P = 0.007). Survival analysis showed that positive p21/WAF1 expression or/and negative MDM2 expression in HCC was a predictor of better survival of patients after tumor resection (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: The proteins p53, p21/WAF1, and MDM2 were overexpressed in all the HCC cases in this study, and p53 and p21/WAF1 overexpression were positively correlated. The expression of p21/WAF1 and MDM2 can be considered as 2 useful indicators for predicting the prognosis of HCC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of Protein Phosphatase 1γ (PP1γ) Is Associated with Enhanced Cell Proliferation and Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 Jan;62(1):133-142. doi: 10.1007/s10620-016-4365-1. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 27921263
-
P21/WAF1 is an independent survival prognostic factor for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after resection.Liver Int. 2007 Aug;27(6):772-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2007.01499.x. Liver Int. 2007. PMID: 17617120
-
Hepatitis C virus-NS3P in relation to p53, p21waf, mdm2, p21-ras and c-erbB2 in hepatocarcinogenesis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005 Nov;20(11):1731-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.04002.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005. PMID: 16246194
-
MDM2-p53 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 15;74(24):7161-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1446. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25477334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the p53-p21 axis in liver cancer: Linking cellular senescence to tumor suppression and progression.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Nov;263:155652. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155652. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39437639 Review.
Cited by
-
RANBP9 suppresses tumor proliferation in colorectal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 May;17(5):4409-4416. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10134. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30988811 Free PMC article.
-
MDM2-p53 Interactions in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What Is the Role of Nutlins and New Therapeutic Options?J Clin Med. 2018 Mar 27;7(4):64. doi: 10.3390/jcm7040064. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 29584707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Murine double minute 2 regulates Hu antigen R stability in human liver and colon cancer through NEDDylation.Hepatology. 2012 Apr;55(4):1237-48. doi: 10.1002/hep.24795. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22095636 Free PMC article.
-
MDM2-NFAT1 dual inhibitor, MA242: Effective against hepatocellular carcinoma, independent of p53.Cancer Lett. 2019 Sep 10;459:156-167. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.114429. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 31181320 Free PMC article.
-
Rictor mediates p53 deactivation to facilitate the malignant transformation of hepatocytes and promote hepatocarcinogenesis.J Transl Med. 2023 Dec 18;21(1):919. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04799-9. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 38110956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Okuda K, Ohtsuki T, Obata H, Tomimatsu M, Okazaki N, Hasegawa H, Nakajima Y, Ohnishi K. Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma and prognosis in relation to treatment. Study of 850 patients. Cancer. 1985;56:918–928. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850815)56:4<918::AID-CNCR2820560437>3.0.CO;2-E. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Michieli P, Chedid M, Lin D, Pierce JH, Mercer WE, Givol D. Induction of WAF1/CIP1 by a p53-independent pathway. Cancer Res. 1994;54:3391–3395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

