Embryonic toxicokinetic and dynamic differences underlying strain sensitivity to cadmium during neurulation
- PMID: 20025959
- PMCID: PMC2855762
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2009.12.004
Embryonic toxicokinetic and dynamic differences underlying strain sensitivity to cadmium during neurulation
Abstract
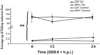
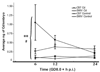
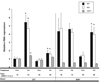
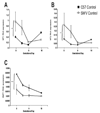
Differences in sensitivity are observed between mouse strains, C57 (sensitive) and SWV (resistant) when exposed to cadmium (Cd) during the neurulation period. In this study, we investigated the toxicokinetics of Cd in relation with toxicodynamic responses to identify factors affecting differential Cd-sensitivity in C57 and SWV. Using a level of exposure which induced developmental toxicity and differential effects between strains, we assessed maternal and embryonic Cd uptake and evaluated biomarkers of response previously linked with Cd exposure, specifically metal ion regulators (Mt1, Mt2, DMT1) and markers of cell cycle arrest/apoptosis induction (p53, Cdkn1a, c-Casp3). Greater Cd uptake was observed in C57 embryos compared to SWV and these observations of differential uptake were associated with increased alterations in expression of biomarkers of metal response (e.g. c-Casp3) and strain sensitivity. Using sensitive and resistant mouse strains, we have identified toxicokinetic and dynamic differences which underlie observed differences in Cd embryonic sensitivity and response.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Arsenic- and cadmium-induced toxicogenomic response in mouse embryos undergoing neurulation.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011 Jan 15;250(2):117-29. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2010.09.018. Epub 2010 Sep 29. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20883709 Free PMC article.
-
Cadmium-induced differential toxicogenomic response in resistant and sensitive mouse strains undergoing neurulation.Toxicol Sci. 2009 Jan;107(1):206-19. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfn221. Epub 2008 Oct 29. Toxicol Sci. 2009. PMID: 18974090 Free PMC article.
-
Methylmercury induced toxicogenomic response in C57 and SWV mouse embryos undergoing neural tube closure.Reprod Toxicol. 2010 Sep;30(2):284-91. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2010.05.009. Epub 2010 May 20. Reprod Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20493249 Free PMC article.
-
[Cadmium induces p53-dependent apoptosis through the inhibition of Ube2d family gene expression].Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2012;67(4):472-7. doi: 10.1265/jjh.67.472. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 23095357 Review. Japanese.
-
Early biomarkers of cadmium exposure and nephrotoxicity.Biometals. 2010 Oct;23(5):793-809. doi: 10.1007/s10534-010-9288-2. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Biometals. 2010. PMID: 20107869 Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental toxicity of cadmium in infants and children: a review.Environ Anal Health Toxicol. 2021 Mar;36(1):e2021003-0. doi: 10.5620/eaht.2021003. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Environ Anal Health Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33730790 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic- and cadmium-induced toxicogenomic response in mouse embryos undergoing neurulation.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011 Jan 15;250(2):117-29. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2010.09.018. Epub 2010 Sep 29. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20883709 Free PMC article.
-
From the Cover: Teratogenic Effects of in Utero Exposure to Di-(2-Ethylhexyl)-Phthalate (DEHP) in B6:129S4 Mice.Toxicol Sci. 2017 May 1;157(1):8-19. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfx019. Toxicol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28123099 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of in Utero Exposure to Arsenic during the Second Half of Gestation on Reproductive End Points and Metabolic Parameters in Female CD-1 Mice.Environ Health Perspect. 2016 Mar;124(3):336-43. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1509703. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Environ Health Perspect. 2016. PMID: 26295903 Free PMC article.
-
Potential frameworks to support evaluation of mechanistic data for developmental neurotoxicity outcomes: A symposium report.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2020 Mar-Apr;78:106865. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2020.106865. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2020. PMID: 32068112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barr M., Jr The teratogenicity of cadmium chloride in two stocks of Wistar rats. Teratology. 1973;7:237–242. - PubMed
-
- Ferm VH. Developmental malformations induced by cadmium. A study of timed injections during embryogenesis. Biology of the neonate. 1971;19:101–107. - PubMed
-
- Brako EE, Wilson AK, Jonah MM, Blum CA, Cerny EA, Williams KL, Bhattacharyya MH. Cadmium pathways during gestation and lactation in control versus metallothoinein 1,2-knockout mice. Toxicological sciences. 2003;71:154–163. - PubMed
-
- Goyer RA. Toxic and essential metal interactions. Annual review of nutrition. 1997;17:37–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

