A long-wavelength fluorescent substrate for continuous fluorometric determination of alpha-mannosidase activity: resorufin alpha-D-mannopyranoside
- PMID: 20026005
- PMCID: PMC2824011
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2009.11.039
A long-wavelength fluorescent substrate for continuous fluorometric determination of alpha-mannosidase activity: resorufin alpha-D-mannopyranoside
Abstract
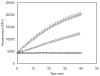
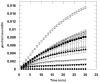
A simple and reliable continuous assay for measurement of alpha-mannosidase activity is described and demonstrated for analysis with two recombinant human enzymes using the new substrate resorufin alpha-d-mannopyranoside (Res-Man). The product of enzyme reaction, resorufin, exhibits fluorescence emission at 585 nm with excitation at 571 nm and has a pK(a) of 5.8, allowing continuous measurement of fluorescence turnover at or near physiological pH values for human lysosomal and Drosophila Golgi alpha-mannosidases. The assay performed using recombinant Drosophila Golgi alpha-mannosidase (dGMII) has been shown to give the kinetic parameters K(m) of 200 microM and V(max) of 11 nmol/min per nmol dGMII. Methods for performing the assay using several concentrations of the known alpha-mannosidase inhibitor swainsonine are also presented, demonstrating a potential for use of the assay as a simple method for high-throughput screening of inhibitors potentially useful in cancer treatment.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster mannosidase II; GMII; Golgi mannosidase II; Res-Man; continuous fluorescent enzyme assay; dGMII; fluorogenic substrate; kinetic assay; resorufin α-D-mannopyranoside.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A long-wavelength fluorescent substrate for continuous fluorometric determination of cellulase activity: resorufin-beta-D-cellobioside.Anal Biochem. 2007 Dec 15;371(2):146-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2007.08.027. Epub 2007 Aug 28. Anal Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17927946
-
Human lysosomal alpha-mannosidases exhibit different inhibition and metal binding properties.Protein Sci. 2009 Nov;18(11):2242-51. doi: 10.1002/pro.235. Protein Sci. 2009. PMID: 19722277 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-guided design of C3-branched swainsonine as potent and selective human Golgi α-mannosidase (GMII) inhibitor.Chem Commun (Camb). 2024 Oct 10;60(82):11734-11737. doi: 10.1039/d4cc04514a. Chem Commun (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39318342
-
Targeting cancer via Golgi α-mannosidase II inhibition: How far have we come in developing effective inhibitors?Carbohydr Res. 2021 Oct;508:108395. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2021.108395. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Carbohydr Res. 2021. PMID: 34280804 Review.
-
Golgi alpha-mannosidase II deficiency in vertebrate systems: implications for asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing in mammals.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Dec 19;1573(3):225-35. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(02)00388-4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12417404 Review.
Cited by
-
High throughput nanostructure-initiator mass spectrometry screening of microbial growth conditions for maximal β-glucosidase production.Front Microbiol. 2013 Dec 6;4:365. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00365. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24367356 Free PMC article.
-
Rotamer-Restricted Fluorogenicity of the Bis-Arsenical ReAsH.J Am Chem Soc. 2016 Jun 8;138(22):7143-50. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b03422. Epub 2016 May 10. J Am Chem Soc. 2016. PMID: 27163487 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the target-specific inhibition of sensitized protein tyrosine phosphatases with biarsenical probes.Org Biomol Chem. 2015 Feb 7;13(5):1395-403. doi: 10.1039/c4ob02256d. Org Biomol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25460004 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a potential allosteric site of Golgi α-mannosidase II using computer-aided drug design.PLoS One. 2019 May 8;14(5):e0216132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216132. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31067280 Free PMC article.
-
Benzylic Trifluoromethyl Accelerates 1,6-Elimination Toward Rapid Probe Activation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 31:2024.05.30.596105. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.30.596105. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38854154 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Bernacki RJ, Niedbala MJ, Korytnyk W. Glycosidases in cancer and invasion. Cancer Meta Rev. 1985;4:81–101. - PubMed
-
- Dennis JW, Granovsky M, Warren CE. Glycoprotein glycosylation and cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1473:21–34. - PubMed
-
- Dube DH, Bertozzi CR. Glycans in cancer and inflammation. Potential for therapeutics and diagnostics. Nat Rev Drug Disc. 2005;4:477–488. - PubMed
-
- Goss PE, Baker ME, Carver JP, Dennis JW. Inhibitors of carbohydrate processing: A new class of anticancer agents. Clin Cancer Res. 1995;1:935–944. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

