Functional analysis of human tRNA isodecoders
- PMID: 20026070
- PMCID: PMC2822071
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.12.018
Functional analysis of human tRNA isodecoders
Abstract
tRNA isodecoders share the same anticodon but have differences in their body sequence. An unexpected result from genome sequencing projects is the identification of a large number of tRNA isodecoder genes in mammalian genomes. In the reference human genome, more than 270 isodecoder genes are present among the approximately 450 tRNA genes distributed among 49 isoacceptor families. Whether sequence diversity among isodecoder tRNA genes reflects functional variability is an open question. To address this, we developed a method to quantify the efficiency of tRNA isodecoders in stop-codon suppression in human cell lines. First, a green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene that contains a single UAG stop codon at two distinct locations is introduced. GFP is only produced when a tRNA suppressor containing CUA anticodon is co-transfected with the GFP gene. The suppression efficiency is examined for 31 tRNA isodecoders (all contain CUA anticodon), 21 derived from four isoacceptor families of tRNASer genes, 7 from five families of tRNALeu genes, and 3 from three families of tRNAAla genes. We found that isodecoder tRNAs display a large difference in their suppression efficiency. Among those with above background suppression activity, differences of up to 20-fold were observed. We were able to tune tRNA suppression efficiency by subtly adjusting the tRNA sequence and inter-convert poor suppressors into potent ones. We also demonstrate that isodecoder tRNAs with varying suppression efficiencies have similar stability and exhibit similar levels of aminoacylation in vivo. Our results indicate that naturally occurring tRNA isodecoders can have large functional variations and suggest that some tRNA isodecoders may perform a function distinct from translation.
Copyright (c) 2009. Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
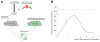
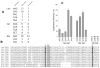
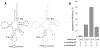



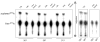

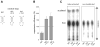
Similar articles
-
Diversity of tRNA genes in eukaryotes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(21):6137-46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl725. Epub 2006 Nov 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 17088292 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing tRNA isodecoders for non-canonical functions via tRNA cleavage.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 4:2024.09.04.611212. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.04.611212. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39282440 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Pyrrolysine encoded by UAG in Archaea: charging of a UAG-decoding specialized tRNA.Science. 2002 May 24;296(5572):1459-62. doi: 10.1126/science.1069588. Science. 2002. PMID: 12029131
-
Diversity of human tRNA genes from the 1000-genomes project.RNA Biol. 2013 Dec;10(12):1853-67. doi: 10.4161/rna.27361. Epub 2013 Dec 9. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 24448271 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli initiator tRNA: structure-function relationships and interactions with the translational machinery.Biochem Cell Biol. 1995 Nov-Dec;73(11-12):1023-31. doi: 10.1139/o95-109. Biochem Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 8722017 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Selection and Functional Potentials of Human Noncoding Elements Revealed by Analysis of Next Generation Sequencing Data.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 8;10(6):e0129023. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129023. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26053627 Free PMC article.
-
LOTTE-seq (Long hairpin oligonucleotide based tRNA high-throughput sequencing): specific selection of tRNAs with 3'-CCA end for high-throughput sequencing.RNA Biol. 2020 Jan;17(1):23-32. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1664250. Epub 2019 Sep 16. RNA Biol. 2020. PMID: 31486704 Free PMC article.
-
tRNA dysregulation and disease.Nat Rev Genet. 2022 Nov;23(11):651-664. doi: 10.1038/s41576-022-00501-9. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Nat Rev Genet. 2022. PMID: 35681060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5'-tiRNA-Gln inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing translation through the interaction with eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-I.Front Med. 2023 Jun;17(3):476-492. doi: 10.1007/s11684-022-0966-6. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Front Med. 2023. PMID: 36973570
-
Chemically modified tRNA enhances the translation capacity of mRNA rich in cognate codons.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 22;16(1):7825. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62981-7. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40846860 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

