Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II contributes to intracellular pH recovery from acidosis via Na(+)/H(+) exchanger activation
- PMID: 20026127
- PMCID: PMC2883686
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.12.007
Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II contributes to intracellular pH recovery from acidosis via Na(+)/H(+) exchanger activation
Abstract
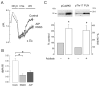
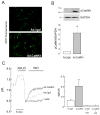
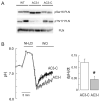
The Na(+)/H(+) exchanger (NHE-1) plays a key role in pH(i) recovery from acidosis and is regulated by pH(i) and the ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation pathway. Since acidosis increases the activity of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) in cardiac muscle, we examined whether CaMKII activates the exchanger by using pharmacological tools and highly specific genetic approaches. Adult rat cardiomyocytes, loaded with the pH(i) indicator SNARF-1/AM were subjected to different protocols of intracellular acidosis. The rate of pH(i) recovery from the acid load (dpH(i)/dt)-an index of NHE-1 activity in HEPES buffer or in NaHCO(3) buffer in the presence of inhibition of anion transporters-was significantly decreased by the CaMKII inhibitors KN-93 or AIP. pH(i) recovery from acidosis was faster in CaMKII-overexpressing myocytes than in overexpressing beta-galactosidase myocytes (dpH(i)/dt: 0.195+/-0.04 vs. 0.045+/-0.010 min(-)(1), respectively, n=8) and slower in myocytes from transgenic mice with chronic cardiac CaMKII inhibition (AC3-I) than in controls (AC3-C). Inhibition of CaMKII and/or ERK1/2 indicated that stimulation of NHE-1 by CaMKII was independent of and additive to the ERK1/2 cascade. In vitro studies with fusion proteins containing wild-type or mutated (Ser/Ala) versions of the C-terminal domain of NHE-1 indicate that CaMKII phosphorylates NHE-1 at residues other than the canonical phosphorylation sites for the kinase (Ser648, Ser703, and Ser796). These results provide new mechanistic insights and unequivocally demonstrate a role of the already multifunctional CaMKII on the regulation of the NHE-1 activity. They also prove clinically important in multiple disorders which, like ischemia/reperfusion injury or hypertrophy, are associated with increased NHE-1 and CaMKII.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: none declared
Figures

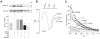

Similar articles
-
Phospholamban is required for CaMKII-dependent recovery of Ca transients and SR Ca reuptake during acidosis in cardiac myocytes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004 Jan;36(1):67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2003.10.012. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 14734049
-
Increased intracellular Ca2+ and SR Ca2+ load contribute to arrhythmias after acidosis in rat heart. Role of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Oct;295(4):H1669-83. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00010.2008. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18723772 Free PMC article.
-
Effects on recovery during acidosis in cardiac myocytes overexpressing CaMKII.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007 Dec;43(6):696-709. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.09.008. Epub 2007 Oct 22. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17950750
-
The myocardial sodium-hydrogen exchanger (NHE) and its role in mediating ischemic and reperfusion injury.Keio J Med. 1998 Jun;47(2):65-72. doi: 10.2302/kjm.47.65. Keio J Med. 1998. PMID: 9659815 Review.
-
Chronic inhibition of na(+)/h(+)-exchanger in the heart.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;4(1):23-9. doi: 10.2174/157016106775203117. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16472174 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Ca2+ signaling motifs that regulate proton signaling through the Na+/H+ exchanger NHX-7 during a rhythmic behavior in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 22;288(8):5886-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.434852. Epub 2013 Jan 14. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23319594 Free PMC article.
-
Chasing cardiac physiology and pathology down the CaMKII cascade.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 May 15;308(10):H1177-91. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00007.2015. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25747749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct cardiac effects of SGLT2 inhibitors.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Mar 18;21(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01480-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35303888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channel Surface Expression in Heart Failure Underlies Dysregulation of Action Potential Duration and Myocardial Vulnerability to Injury.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 10;11(3):e0151337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151337. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26964104 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CaMKII regulation of phospholamban activity in heart disease.Front Pharmacol. 2014 Jan 27;5:5. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00005. eCollection 2014. Front Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24550830 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cingolani HE, Ennis IL. Sodium-hydrogen exchanger, cardiac overload, and myocardial hypertrophy. Circulation. 2007;115:1090–100. - PubMed
-
- Vaughan-Jones RD, Spitzer KW, Swietach P. Intracellular pH regulation in heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009;46:318–31. - PubMed
-
- Avkiran M, Gross G, Karmazyn M, Klein H, Murphy E, Ytrehus K. Na+/H+ exchange in ischemia, reperfusion and preconditioning. Cardiovasc Res. 2001;50:162–6. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi E, Abe J, Gallis B, Aebersold R, Spring DJ, Krebs EG, Berk BC. p90(RSK) is a serum-stimulated Na+/H+ exchanger isoform-1 kinase. Regulatory phosphorylation of serine 703 of Na+/H+ exchanger isoform-1. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:20206–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

