Agonist-induced restoration of hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive improvement in a model of cholinergic denervation
- PMID: 20026137
- PMCID: PMC4517434
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.12.005
Agonist-induced restoration of hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive improvement in a model of cholinergic denervation
Abstract
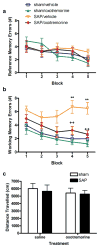
Loss of basal forebrain cholinergic innervation of the hippocampus and severe neuronal loss within the hippocampal CA1 region are early hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease, and are strongly correlated with cognitive status. Various therapeutic approaches involve attempts to enhance neurotransmission or to provide some level of neuroprotection for remaining cells. An alternative approach may involve the generation of new cells to replace those lost in AD. Indeed, a simple shift in the balance between cell generation and cell loss may slow disease progression and possibly even reverse existing cognitive deficits. One potential neurogenic regulator might be acetylcholine, itself, which has been shown to play a critical role in hippocampal development. Here, we report the effects of various cholinergic compounds on indices of hippocampal neurogenesis, demonstrating a significant induction following pharmacological activation of muscarinic M1 receptors, located on hippocampal progenitors in the adult brain. This is the first report that a small-molecule agonist may induce neurogenesis in the hippocampal CA1 region. Furthermore, such treatment reversed deficits in markers of neurogenesis and spatial working memory triggered by cholinergic denervation in a rodent model. This study suggests the use of small molecule, receptor agonists may represent a novel means to trigger the restoration of specific neuronal populations lost to a variety of neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, Huntington's and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
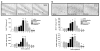
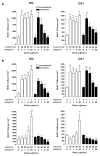
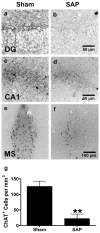
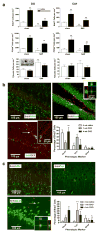
Similar articles
-
Effects of Selective M1 Muscarinic Receptor Activation on Hippocampal Spatial Representations and Neuronal Oscillations.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016 Oct 19;7(10):1393-1405. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00160. Epub 2016 Aug 12. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27479319
-
Intraseptal muscarinic ligands and galanin: influence on hippocampal acetylcholine and cognition.Neuroscience. 2004;126(3):541-57. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.03.058. Neuroscience. 2004. PMID: 15183504
-
Counteractive effects of a partial (sabcomeline) and a full (RS86) muscarinic receptor agonist on deficits in radial maze performance induced by S-AMPA lesions of the basal forebrain and medial septal area.Behav Brain Res. 1999 Feb 15;99(1):81-92. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(98)00075-8. Behav Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10512575
-
Muscarinic receptor pharmacology and circuitry for the modulation of cognition.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2012;(208):121-66. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-23274-9_7. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22222698 Review.
-
M1 muscarinic agonists can modulate some of the hallmarks in Alzheimer's disease: implications in future therapy.J Mol Neurosci. 2003;20(3):349-56. doi: 10.1385/JMN:20:3:349. J Mol Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14501019 Review.
Cited by
-
Alterations in Cholinergic Pathways and Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Cholinergic System after Traumatic Brain Injury.J Neurotrauma. 2015 Oct 1;32(19):1429-40. doi: 10.1089/neu.2014.3445. Epub 2015 Jun 29. J Neurotrauma. 2015. PMID: 25646580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extended access nicotine self-administration with periodic deprivation increases immature neurons in the hippocampus.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Jan;232(2):453-63. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3685-0. Epub 2014 Jul 26. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25059540 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Activity-Dependent Control of Postnatal Neurogenesis and Gliogenesis.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2018 Jul 8;41:139-161. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-072116-031054. Epub 2018 Apr 4. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29618286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus by stress, acetylcholine and dopamine.J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2011 Jan;2(1):26-37. doi: 10.4103/0976-9668.82312. J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 22470231 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Neurotransmitter Shifting during Neurogenesis and Neurodegeneration of PC12 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 27;25(19):10399. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910399. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abood LG, Saraswati M, Lerner-Marmarosh N, Hashmi M. Affinity ligands and related agents for brain muscarinic and nicotinic cholinergic receptors. Biochemical Pharmacology. 1993;45:2143–2148. - PubMed
-
- Ball MJ. Neuronal loss, neurofibrillary tangles and granulovacuolar degeneration in the hippocampus with ageing and dementia. Acta Neuropathologica. 1977;37:111–118. - PubMed
-
- Barker JL, Behar T, Li YX, Liu QY, Ma W, Maric D, Maric I, Schaffner AE, Serafini R, Smith SV, Somogyi R, Vautrin JY, Wen XL, Xian H. GABAergic cells and signals in CNS development. Perspectives on Developmental Neurobiology. 1998;5:305–322. - PubMed
-
- Bobinski M, de Leon MJ, Tarnawski M, Wegiel J, Bobinski M, Reisberg B, Miller DC, Wisniewski HM. Neuronal and volume loss in CA1 of the hippocampal formation uniquely predicts duration and severity of Alzheimer disease. Brain Research. 1998;805:267–269. - PubMed
-
- Borta A, Hoglinger GU. Dopamine and adult neurogenesis. Journal of Neurochemistry. 2007;100:587–595. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

