Protein kinase A regulation of P2X(4) receptors: requirement for a specific motif in the C-terminus
- PMID: 20026202
- PMCID: PMC2839067
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.12.002
Protein kinase A regulation of P2X(4) receptors: requirement for a specific motif in the C-terminus
Abstract
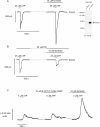
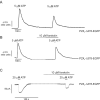
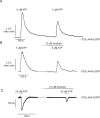
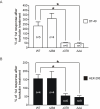
The P2X purinergic receptor sub-family of ligand-gated ion channels are subject to protein kinase modulation. We have previously demonstrated that P2X(4)R signaling can be positively regulated by increasing intracellular cAMP levels. The molecular mechanism underlying this effect was, however, unknown. The present study initially addressed whether protein kinase A (PKA) activation was required. Subsequently a mutational approach was utilized to determine which region of the receptor was required for this potentiation. In both DT-40 3KO and HEK-293 cells transiently expressing P2X(4)R, forskolin treatment enhanced ATP-mediated signaling. Specific PKA inhibitors prevented the forskolin-induced enhancement of ATP-mediated inward currents in P2X(4)R expressing HEK-293 cells. To define which region of the P2X(4)R was required for the potentiation, mutations were generated in the cytoplasmic C-terminal tail. It was determined that a limited region of the C-terminus, consisting of a non-canonical tyrosine based sorting motif, was required for the effects of PKA. Of note, this region does not harbor any recognizable PKA phosphorylation motifs, and no direct phosphorylation of P2X(4)R was detected, suggesting that PKA phosphorylation of an accessory protein interacts with the endocytosis motif in the C-terminus of the P2X(4)R. In support of this notion, using Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Microscopy (TIRF)\ P2X(4)-EGFP was shown to accumulate at/near the plasma membrane following forskolin treatment. In addition, disrupting the endocytosis machinery using a dominant-negative dynamin construct also prevented the PKA-mediated enhancement of ATP-stimulated Ca(2+) signals. Our results are consistent with a novel mechanism of P2XR regulation, whereby PKA activity, without directly phosphorylating P2X(4)R, markedly enhances ATP-stimulated P2X(4)R currents and hence cytosolic Ca(2+) signals. This may occur at least in part, by altering the trafficking of a population of P2X(4)R present at the plasma membrane.
Figures





Similar articles
-
cAMP potentiates ATP-evoked calcium signaling in human parotid acinar cells.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 17;279(38):39485-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406201200. Epub 2004 Jul 19. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15262999
-
Protein kinase C regulation of P2X3 receptors is unlikely to involve direct receptor phosphorylation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Feb;1773(2):166-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.09.020. Epub 2006 Sep 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17052768 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the abused solvent toluene on recombinant P2X receptors expressed in HEK293 cells.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004 Jun 18;125(1-2):86-95. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.03.005. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15193425
-
Functional modulation of P2X2 receptors by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase.J Neurochem. 1998 Jun;70(6):2606-12. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70062606.x. J Neurochem. 1998. PMID: 9603227
-
Assembly and trafficking of P2X purinergic receptors (Review).Mol Membr Biol. 2008 May;25(4):321-31. doi: 10.1080/09687680802050385. Mol Membr Biol. 2008. PMID: 18446618 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of P2X1 receptors by modulators of the cAMP effectors PKA and EPAC.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 14;118(37):e2108094118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2108094118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34508006 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Talk Between the Adenylyl Cyclase/cAMP Pathway and Ca2+ Homeostasis.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;179:73-116. doi: 10.1007/112_2020_55. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33398503 Review.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 modulates the P2X2a receptor channel gating through phosphorylation of C-terminal threonine 372.Pain. 2017 Nov;158(11):2155-2168. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001021. Pain. 2017. PMID: 28809765 Free PMC article.
-
CB1 Receptors Mediated Inhibition of ATP-Induced [Ca2+]i Increase in Cultured Rat Spinal Dorsal Horn Neurons.Neurochem Res. 2018 Feb;43(2):267-275. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2414-6. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29127599
-
Resolving the Ionotropic P2X4 Receptor Mystery Points Towards a New Therapeutic Target for Cardiovascular Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 15;21(14):5005. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145005. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32679900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schwiebert EM, Zsembery A. Extracellular ATP as a signaling molecule for epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1615:7–32. - PubMed
-
- North RA. Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:1013–67. - PubMed
-
- Turner JT, Landon LA, Gibbons SJ, Talamo BR. Salivary gland P2 nucleotide receptors. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1999;10:210–24. - PubMed
-
- Brake AJ, Wagenbach MJ, Julius D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature. 1994;371:519–23. - PubMed
-
- Khakh BS, North RA. P2X receptors as cell-surface ATP sensors in health and disease. Nature. 2006;442:527–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

