Protein deacetylation by SIRT1: an emerging key post-translational modification in metabolic regulation
- PMID: 20026274
- PMCID: PMC3620551
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2009.12.006
Protein deacetylation by SIRT1: an emerging key post-translational modification in metabolic regulation
Abstract
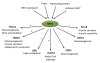
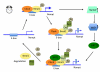
The biological function of most proteins relies on reversible post-translational modifications, among which phosphorylation is most prominently studied and well recognized. Recently, a growing amount of evidence indicates that acetylation-deacetylation reactions, when applied to crucial mediators, can also robustly affect the function of target proteins and thereby have wide-ranging physiological impacts. Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), which functions as a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD(+))-dependent protein deacetylase, deacetylates a wide variety of metabolic molecules in response to the cellular energy and redox status and as such causes significant changes in metabolic homeostasis. This review surveys the evidence for the emerging role of SIRT1-mediated deacetylation in the control of metabolic homeostasis.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A p300 and SIRT1 Regulated Acetylation Switch of C/EBPα Controls Mitochondrial Function.Cell Rep. 2018 Jan 9;22(2):497-511. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.12.061. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29320743
-
Obesity and aging diminish sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)-mediated deacetylation of SIRT3, leading to hyperacetylation and decreased activity and stability of SIRT3.J Biol Chem. 2017 Oct 20;292(42):17312-17323. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.778720. Epub 2017 Aug 14. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28808064 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of SIRT1 by L-serine increases fatty acid oxidation and reverses insulin resistance in C2C12 myotubes.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2019 Oct;35(5):457-470. doi: 10.1007/s10565-019-09463-x. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30721374
-
SIRT1-dependent regulation of chromatin and transcription: linking NAD(+) metabolism and signaling to the control of cellular functions.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1804(8):1666-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.10.022. Epub 2009 Oct 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19879981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-talk between SIRT1 and endocrine factors: effects on energy homeostasis.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 Nov;397(1-2):42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.08.002. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25109279 Review.
Cited by
-
Hugan Qingzhi Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects in a Rat Model of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:810369. doi: 10.1155/2015/810369. Epub 2015 Jun 14. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26146507 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin biology and relevance to diabetes treatment.Diabetes Manag (Lond). 2012 May;2(3):243-257. doi: 10.2217/dmt.12.16. Diabetes Manag (Lond). 2012. PMID: 23024708 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Resveratrol on Pregnancy, Prenatal Complications and Pregnancy-Associated Structure Alterations.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;12(2):341. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020341. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-fat diet-induced impairment of skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity is not prevented by SIRT1 overexpression.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Nov 1;307(9):E764-72. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00001.2014. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 25159328 Free PMC article.
-
Leucine supplementation increases SIRT1 expression and prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic disorders in high-fat diet-induced obese mice.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Nov 15;303(10):E1234-44. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00198.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22967499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glozak MA, Sengupta N, Zhang X, Seto E. Acetylation and deacetylation of non-histone proteins. Gene. 2005;363:15–23. - PubMed
-
- Kim SC, Sprung R, Chen Y, Xu Y, Ball H, Pei J, Cheng T, Kho Y, Xiao H, Xiao L, Grishin NV, White M, Yang XJ, Zhao Y. Substrate and functional diversity of lysine acetylation revealed by a proteomics survey. Mol Cell. 2006;23:607–618. - PubMed
-
- Choudhary C, Kumar C, Gnad F, Nielsen ML, Rehman M, Walther TC, Olsen JV, Mann M. Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science. 2009;325:834–840. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

