Overcoming rapid inactivation of lung surfactant: analogies between competitive adsorption and colloid stability
- PMID: 20026298
- PMCID: PMC2834873
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.12.010
Overcoming rapid inactivation of lung surfactant: analogies between competitive adsorption and colloid stability
Abstract
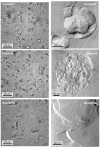
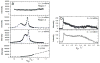
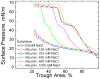
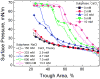
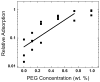
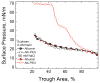
Lung surfactant (LS) is a mixture of lipids and proteins that line the alveolar air-liquid interface, lowering the interfacial tension to levels that make breathing possible. In acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), inactivation of LS is believed to play an important role in the development and severity of the disease. This review examines the competitive adsorption of LS and surface-active contaminants, such as serum proteins, present in the alveolar fluids of ARDS patients, and how this competitive adsorption can cause normal amounts of otherwise normal LS to be ineffective in lowering the interfacial tension. LS and serum proteins compete for the air-water interface when both are present in solution either in the alveolar fluids or in a Langmuir trough. Equilibrium favors LS as it has the lower equilibrium surface pressure, but the smaller proteins are kinetically favored over multi-micron LS bilayer aggregates by faster diffusion. If albumin reaches the interface, it creates an energy barrier to subsequent LS adsorption that slows or prevents the adsorption of the necessary amounts of LS required to lower surface tension. This process can be understood in terms of classic colloid stability theory in which an energy barrier to diffusion stabilizes colloidal suspensions against aggregation. This analogy provides qualitative and quantitative predictions regarding the origin of surfactant inactivation. An important corollary is that any additive that promotes colloid coagulation, such as increased electrolyte concentration, multivalent ions, hydrophilic non-adsorbing polymers such as PEG, dextran, etc. added to LS, or polyelectrolytes such as chitosan, also promotes LS adsorption in the presence of serum proteins and helps reverse surfactant inactivation. The theory provides quantitative tools to determine the optimal concentration of these additives and suggests that multiple additives may have a synergistic effect. A variety of physical and chemical techniques including isotherms, fluorescence microscopy, electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction show that LS adsorption is enhanced by this mechanism without substantially altering the structure or properties of the LS monolayer.
Keywords: Debye length; albumin; charge reversal; chitosan; depletion attraction; inhibition; polyethylene glycol.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures












References
-
- Bastacky J, Lee CY, Goerke J, Koushafar H, Yager D, Speed TP, Chen Y, Clements JA. Alveolar lining layer is thin and continuous: low temperature scanning electron microscopy of rat lung. J Applied Physiology. 1995;79:1615–1628. - PubMed
-
- Clements JA, Avery ME. Lung surfactant and neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 1998;157:S59–S66. - PubMed
-
- Notter R. Lung surfactant: basic science and clinical applications. Marcel Dekker; New York: 2000.
-
- Perez-Gil J. Structure of pulmonary surfactant membranes and films: the role of proteins and lipid-protein interactions. Biochimica et Biophysica acta (BBA)-Biomembranes. 2008;1778:1676–1695. - PubMed
-
- Zasadzinski JA, Ding J, Warriner HE, Bringezu F, Waring AJ. The physics and physiology of lung surfactants. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science. 2001;6:506–513.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

