The ferritin superfamily: Supramolecular templates for materials synthesis
- PMID: 20026386
- PMCID: PMC3763752
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.12.005
The ferritin superfamily: Supramolecular templates for materials synthesis
Abstract
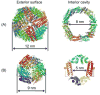
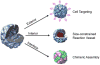
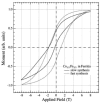
Members of the ferritin superfamily are multi-subunit cage-like proteins with a hollow interior cavity. These proteins possess three distinct surfaces, i.e. interior and exterior surfaces of the cages and interface between subunits. The interior cavity provides a unique reaction environment in which the interior reaction is separated from the external environment. In biology the cavity is utilized for sequestration of irons and biomineralization as a mechanism to render Fe inert and sequester it from the external environment. Material scientists have been inspired by this system and exploited a range of ferritin superfamily proteins as supramolecular templates to encapsulate nanoparticles and/or as well-defined building blocks for fabrication of higher order assembly. Besides the interior cavity, the exterior surface of the protein cages can be modified without altering the interior characteristics. This allows us to deliver the protein cages to a targeted tissue in vivo or to achieve controlled assembly on a solid substrate to fabricate higher order structures. Furthermore, the interface between subunits is utilized for manipulating chimeric self-assembly of the protein cages and in the generation of symmetry-broken Janus particles. Utilizing these ideas, the ferritin superfamily has been exploited for development of a broad range of materials with applications from biomedicine to electronics.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





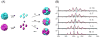
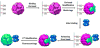
References
-
- Koeck PJB, Kagawa HK, Ellis MJ, Hebert H, Trent JD. Two-dimensional crystals of reconstituted .beta.-subunits of the chaperonin TF55 from Sulfolobus shibatae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1429:40–44. - PubMed
-
- Trent JD. A review of acquired thermotolerance, heat-shock proteins, and molecular chaperones in archaea. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1996;18:249–258.
-
- Kim KK, Kim R, Kim SH. Crystal structure of a small heat-shock protein. Nature. 1998;394:595–599. - PubMed
-
- Bozzi M, Mignogna G, Stefanini S, Barra D, Longhi C, Valenti P, Chiancone E. A Novel Non-heme Iron-binding Ferritin Related to the DNA-binding Proteins of the Dps Family in Listeria innocua. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:3259–3265. - PubMed
-
- Grant RA, Filman DJ, Finkel SE, Kolter R, Hogle JM. The crystal structure of Dps, a ferritin homolog that binds and protects DNA. Nature Structural Biology. 1998;5:294–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

