Decision-making during gambling: an integration of cognitive and psychobiological approaches
- PMID: 20026469
- PMCID: PMC2827449
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0147
Decision-making during gambling: an integration of cognitive and psychobiological approaches
Abstract
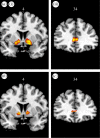
Gambling is a widespread form of entertainment that may afford unique insights into the interaction between cognition and emotion in human decision-making. It is also a behaviour that can become harmful, and potentially addictive, in a minority of individuals. This article considers the status of two dominant approaches to gambling behaviour. The cognitive approach has identified a number of erroneous beliefs held by gamblers, which cause them to over-estimate their chances of winning. The psychobiological approach has examined case-control differences between groups of pathological gamblers and healthy controls, and has identified dysregulation of brain areas linked to reward and emotion, including the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) and striatum, as well as alterations in dopamine neurotransmission. In integrating these two approaches, recent data are discussed that reveal anomalous recruitment of the brain reward system (including the vmPFC and ventral striatum) during two common cognitive distortions in gambling games: the near-miss effect and the effect of personal control. In games of chance, near-misses and the presence of control have no objective influence on the likelihood of winning. These manipulations appear to harness a reward system that evolved to learn skill-oriented behaviours, and by modulating activity in this system, these cognitive distortions may promote continued, and potentially excessive, gambling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Games in the Brain: Neural Substrates of Gambling Addiction.Neuroscientist. 2016 Oct;22(5):534-45. doi: 10.1177/1073858415591474. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Neuroscientist. 2016. PMID: 26116634 Review.
-
Gambling severity predicts midbrain response to near-miss outcomes.J Neurosci. 2010 May 5;30(18):6180-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5758-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20445043 Free PMC article.
-
Decision-Making, Cognitive Distortions and Alcohol Use in Adolescent Problem and Non-problem Gamblers: An Experimental Study.J Gambl Stud. 2016 Dec;32(4):1203-1213. doi: 10.1007/s10899-016-9597-7. J Gambl Stud. 2016. PMID: 26894884
-
Striatal connectivity changes following gambling wins and near-misses: Associations with gambling severity.Neuroimage Clin. 2014 Jul 3;5:232-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.06.008. eCollection 2014. Neuroimage Clin. 2014. PMID: 25068112 Free PMC article.
-
Gamble with Your Head and Not Your Heart: A Conceptual Model for How Thinking-Style Promotes Irrational Gambling Beliefs.J Gambl Stud. 2020 Mar;36(1):183-206. doi: 10.1007/s10899-019-09927-z. J Gambl Stud. 2020. PMID: 31912382 Review.
Cited by
-
Two-group randomised, parallel trial of cognitive and exposure therapies for problem gambling: a research protocol.BMJ Open. 2013 Jun 28;3(6):e003244. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003244. BMJ Open. 2013. PMID: 23811176 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay between chasing behavior, time perspective, and gambling severity: An experimental study.J Behav Addict. 2019 Jun 1;8(2):259-267. doi: 10.1556/2006.8.2019.29. Epub 2019 Jun 7. J Behav Addict. 2019. PMID: 31172815 Free PMC article.
-
Impulsivity, Gambling-Related Cognitions, Cognitive Reappraisal and Gambling Behaviour in a Malaysian Sample.J Gambl Stud. 2024 Jun;40(2):475-492. doi: 10.1007/s10899-023-10246-7. Epub 2023 Aug 7. J Gambl Stud. 2024. PMID: 37544960 Free PMC article.
-
Living in the Now: Decision-Making and Delay Discounting in Adolescent Gamblers.J Gambl Stud. 2016 Dec;32(4):1191-1202. doi: 10.1007/s10899-016-9595-9. J Gambl Stud. 2016. PMID: 26879947
-
Gambling in Sub-Saharan Africa: Traditional Forms and Emerging Technologies.Curr Addict Rep. 2022;9(4):373-384. doi: 10.1007/s40429-022-00449-0. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Curr Addict Rep. 2022. PMID: 36312763 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association 2000Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders—text revision, 4th edn.Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association
-
- Anderson G., Brown R. I.1984Real and laboratory gambling, sensation-seeking and arousal. Br. J. Psychol. 75, 401–410 - PubMed
-
- Anderson S. W., Damasio H., Jones R. D., Tranel D.1991Wisconsin card sorting test performance as a measure of frontal lobe damage. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 13, 909–922 (doi:10.1080/01688639108405107) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baboushkin H. R., Hardoon K. R., Derevensky J. L., Gupta R.2001Underlying cognitions in gambling behaviour among university students. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 31, 1409–1430 (doi:10.1111/j.1559-1816.2001.tb02680.x) - DOI
-
- Bechara A.2003Risky business: emotion, decision-making, and addiction. J. Gambl. Stud. 19, 23–51 (doi:10.1023/A:1021223113233) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

