Integration of in vivo genotoxicity and short-term carcinogenicity assays using F344 gpt delta transgenic rats: in vivo mutagenicity of 2,4-diaminotoluene and 2,6-diaminotoluene structural isomers
- PMID: 20026473
- PMCID: PMC2819973
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfp306
Integration of in vivo genotoxicity and short-term carcinogenicity assays using F344 gpt delta transgenic rats: in vivo mutagenicity of 2,4-diaminotoluene and 2,6-diaminotoluene structural isomers
Abstract
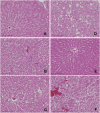
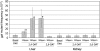
An important trend in current toxicology is the replacement, reduction, and refinement of the use of experimental animals (the 3R principle). We propose a model in which in vivo genotoxicity and short-term carcinogenicity assays are integrated with F344 gpt delta transgenic rats. Using this model, the genotoxicity of chemicals can be identified in target organs using a shuttle vector lambda EG10 that carries reporter genes for mutations; short-term carcinogenicity is determined by the formation of glutathione S-transferase placenta form (GST-P) foci in the liver. To begin validating this system, we examined the genotoxicity and hepatotoxicity of structural isomers of 2,4-diaminotoluene (2,4-DAT) and 2,6-diaminotoluene (2,6-DAT). Although both compounds are genotoxic in the Ames/Salmonella assay, only 2,4-DAT induces tumors in rat livers. Male F344 gpt delta rats were fed diet containing 2,4-DAT at doses of 125, 250, or 500 ppm for 13 weeks or 2,6-DAT at a dose of 500 ppm for the same period. The mutation frequencies of base substitutions, mainly at G:C base pairs, were significantly increased in the livers of 2,4-DAT-treated rats at all three doses. In contrast, virtually no induction of genotoxicity was identified in the kidneys of 2,4-DAT-treated rats or in the livers of 2,6-DAT-treated rats. GST-P-positive foci were detected in the livers of rats treated with 2,4-DAT at a dose of 500 ppm but not in those treated with 2,6-DAT. Integrated genotoxicity and short-term carcinogenicity assays may be useful for early identifying genotoxic and nongenotoxic carcinogens in a reduced number of experimental animals.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genotoxic and non-genotoxic activities of 2,4- and 2,6-diaminotoluene, as evaluated in Fischer-344 rat liver.Toxicology. 1995 May 5;99(1-2):1-10. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(95)02976-f. Toxicology. 1995. PMID: 7761993
-
Quantitative analysis of mutagenicity and carcinogenicity of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline in F344 gpt delta transgenic rats.Mutagenesis. 2019 Sep 20;34(3):279-287. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gez015. Mutagenesis. 2019. PMID: 31233596
-
Differential in vivo mutagenicity of the carcinogen/non-carcinogen pair 2,4- and 2,6-diaminotoluene.Carcinogenesis. 1995 Oct;16(10):2429-33. doi: 10.1093/carcin/16.10.2429. Carcinogenesis. 1995. PMID: 7586147
-
Cell proliferation as a determining factor for the carcinogenicity of chemicals: studies with mutagenic carcinogens and mutagenic noncarcinogens.Toxicol Lett. 1995 Dec;82-83:9-14. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(95)03464-1. Toxicol Lett. 1995. PMID: 8597159 Review.
-
Qualitative and quantitative approaches in the dose-response assessment of genotoxic carcinogens.Mutagenesis. 2016 May;31(3):341-6. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gev049. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Mutagenesis. 2016. PMID: 26152227 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic integration of lambda EG10 transgene in gpt delta transgenic rodents.Genes Environ. 2015 Dec 1;37:24. doi: 10.1186/s41021-015-0024-6. eCollection 2015. Genes Environ. 2015. PMID: 27350819 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Open Tubular Capillary Electrochromatographic Method for Differentiating the DNA Interaction Affinity of Environmental Contaminants.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 7;11(4):e0153081. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153081. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27055261 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic rat models for mutagenesis and carcinogenesis.Genes Environ. 2017 Feb 1;39:11. doi: 10.1186/s41021-016-0072-6. eCollection 2017. Genes Environ. 2017. PMID: 28174618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concordance between Results of Medium-term Liver Carcinogenesis Bioassays and Long-term Findings for Carcinogenic 2-Nitropropane and Non-carcinogenic1-Nitropropane in F344 Rats.J Toxicol Pathol. 2011 Dec;24(4):207-13. doi: 10.1293/tox.24.207. Epub 2012 Jan 7. J Toxicol Pathol. 2011. PMID: 22319232 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Medium-term Animal Model Using gpt Delta Rats to Evaluate Chemical Carcinogenicity and Genotoxicity.J Toxicol Pathol. 2013 Mar;26(1):19-27. doi: 10.1293/tox.26.19. Epub 2013 Apr 22. J Toxicol Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23723564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoki Y, Hashimoto AH, Amanuma K, Matsumoto M, Hiyoshi K, Takano H, Masumura K, Itoh K, Nohmi T, Yamamoto M. Enhanced spontaneous and benzo(a)pyrene-induced mutations in the lung of Nrf2-deficient gpt delta mice. Cancer Res. 2007;67:5643–5648. - PubMed
-
- Bagnyukova TV, Tryndyak VP, Montgomery B, Churchwell MI, Karpf AR, James SR, Muskhelishveli L, Beland FA, Pogribny IP. Genetic and epigenetic changes in rat preneoplastic liver tissue induced by 2-acetylaminofluorene. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:638–646. - PubMed
-
- Balls M. The three Rs concept of alternatives to animal experimentation. In: van Zutphen LFM, Balls M, editors. Animal Alternatives. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1997. pp. 27–41.
-
- Cunningham ML, Burka LT, Matthews HB. Metabolism, disposition, and mutagenicity of 2,6-diaminotoluene, a mutagenic noncarcinogen. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1989;17:612–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

