The ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-1 is required for heart development and is a suppressor of thrombospondin-1
- PMID: 20026598
- PMCID: PMC2825471
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.082347
The ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-1 is required for heart development and is a suppressor of thrombospondin-1
Abstract
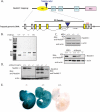
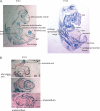
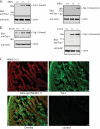
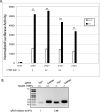
Nedd4 (Nedd4-1) is a Hect domain E3 ubiquitin ligase that also contains a C2 domain and three WW domains. Despite numerous in vitro studies, its biological function in vivo is not well understood. Here we show that disruption of Nedd4-1 in mice (leaving Nedd4-2 intact) caused embryonic lethality at mid gestation, with pronounced heart defects (double-outlet right ventricle and atrioventricular cushion defects) and vasculature abnormalities. Quantitative mass spectrometry and immunoblot analyses of lysates from the wild type and knock-out mouse embryonic fibroblasts to identify Nedd4-1 in vivo targets revealed dramatically increased amounts of thrombospondin-1 (Tsp-1) in the knock-out mouse embryonic fibroblasts and embryos. Tsp-1 is an inhibitor of angiogenesis, and its elevated level was mediated primarily by enhanced transcription. Interestingly, the administration of aspirin (an inhibitor of Tsp-1) to the pregnant heterozygote mothers led to a reduction in Tsp-1 levels and a substantial rescue of the embryonic lethality. These results suggest that Nedd4-1 is a suppressor of Tsp1 and that increased levels of Tsp-1 in the Nedd4-1 knock-out mice may have contributed to the developmental defect observed in the embryos.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of the catalytic regulation of NEDD4-1 and WWP2 ubiquitin ligases.J Biol Chem. 2019 Nov 15;294(46):17421-17436. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009211. Epub 2019 Oct 2. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31578285 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal knockout of Nedd4 enhances growth of Apcmin tumors.Oncogene. 2016 Nov 10;35(45):5839-5849. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.125. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 27086928
-
The Nedd4-like ubiquitin E3 ligases target angiomotin/p130 to ubiquitin-dependent degradation.Biochem J. 2012 Jun 1;444(2):279-89. doi: 10.1042/BJ20111983. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22385262
-
NEDD4: The founding member of a family of ubiquitin-protein ligases.Gene. 2015 Feb 25;557(2):113-22. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.12.020. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25527121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Nedd4-like family of E3 ubiquitin ligases and cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007 Dec;26(3-4):587-604. doi: 10.1007/s10555-007-9091-x. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007. PMID: 17726579 Review.
Cited by
-
Positive association between aspirin-intolerant asthma and genetic polymorphisms of FSIP1: a case-case study.BMC Pulm Med. 2010 Jun 1;10:34. doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-10-34. BMC Pulm Med. 2010. PMID: 20513247 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of ERBB3/HER3 signaling in cancer.Oncotarget. 2014 Nov 15;5(21):10222-36. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2655. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25400118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HECT domain-containing E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4L negatively regulates Wnt signaling by targeting dishevelled for proteasomal degradation.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 22;288(12):8289-8298. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.433185. Epub 2013 Feb 9. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23396981 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-1 participates in denervation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46427. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046427. Epub 2012 Oct 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23110050 Free PMC article.
-
Obestatin signalling counteracts glucocorticoid-induced skeletal muscle atrophy via NEDD4/KLF15 axis.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021 Apr;12(2):493-505. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12677. Epub 2021 Mar 9. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021. PMID: 33687156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glickman M. H., Ciechanover A. (2002) Physiol. Rev. 82, 373–428 - PubMed
-
- Hicke L., Schubert H. L., Hill C. P. (2005) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 610–621 - PubMed
-
- Polo S., Di Fiore P. P. (2006) Cell 124, 897–900 - PubMed
-
- Kumar S., Tomooka Y., Noda M. (1992) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 185, 1155–1161 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

