Intended transcriptional silencing with siRNA results in gene repression through sequence-specific off-targeting
- PMID: 20026621
- PMCID: PMC2811671
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1808510
Intended transcriptional silencing with siRNA results in gene repression through sequence-specific off-targeting
Abstract
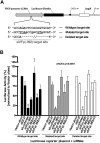
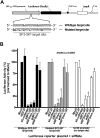
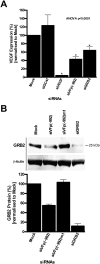
Transcriptional gene silencing has been reported with siRNA targeting the promoter region of genes. We tested several siRNAs directed against the human VEGF promoter. Of these, siVFp(-992) exhibited > or =50% suppression of VEGF production in two human cell lines. To determine the specificity of this siRNA-mediated suppression, plasmids were prepared to express a luciferase reporter under the control of VEGF promoters featuring wild-type, mutated, or deleted target sequences. siRNA transfection assays established sequence-specific inhibition of luciferase from the reporter plasmid featuring the wild-type VEGF promoter. However, siVFp(-992) also suppressed the luciferase expression from the plasmids with mutated or deleted target sites, suggesting that silencing was due to a sequence-specific off-target phenomenon, and this was supported by subsequent microarray and bioinformatics analyses. To determine if our concerns regarding the specificity of promoter targeting siRNAs were relevant to other systems where RNA-mediated transcriptional silencing had been previously reported, we tested a published small RNA sequence directed to the HIV(SF2)-LTR promoter. siRNA transfection assays performed in human cells expressing a luciferase reporter gene under the control of the HIV(SF2)-LTR promoter revealed significant suppression whether the target sequence was intact or mutated, or when the entire HIV(SF2)-LTR was replaced by an irrelevant promoter. These data stress the need to examine target specificity when conducting investigations into transcriptional gene regulation with siRNA.
Figures
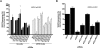
References
-
- Anonymous. Whither RNAi? Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:489–490. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409:363–366. - PubMed
-
- Birmingham A, Anderson EM, Reynolds A, Ilsley-Tyree D, Leake D, Fedorov Y, Baskerville S, Maksimova E, Robinson K, Karpilow J, et al. 3′ UTR seed matches, but not overall identity, are associated with RNAi off-targets. Nat Methods. 2006;3:199–204. - PubMed
-
- Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:185–193. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
