A novel intermembrane space-targeting signal docks cysteines onto Mia40 during mitochondrial oxidative folding
- PMID: 20026652
- PMCID: PMC2806287
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200905134
A novel intermembrane space-targeting signal docks cysteines onto Mia40 during mitochondrial oxidative folding
Abstract
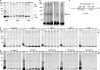
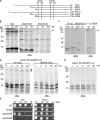
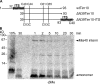
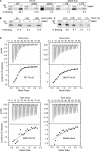
Mia40 imports Cys-containing proteins into the mitochondrial intermembrane space (IMS) by ensuring their Cys-dependent oxidative folding. In this study, we show that the specific Cys of the substrate involved in docking with Mia40 is substrate dependent, the process being guided by an IMS-targeting signal (ITS) present in Mia40 substrates. The ITS is a 9-aa internal peptide that (a) is upstream or downstream of the docking Cys, (b) is sufficient for crossing the outer membrane and for targeting nonmitochondrial proteins, (c) forms an amphipathic helix with crucial hydrophobic residues on the side of the docking Cys and dispensable charged residues on the other side, and (d) fits complementary to the substrate cleft of Mia40 via hydrophobic interactions of micromolar affinity. We rationalize the dual function of Mia40 as a receptor and an oxidase in a two step-specific mechanism: an ITS-guided sliding step orients the substrate noncovalently, followed by docking of the substrate Cys now juxtaposed to pair with the Mia40 active Cys.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The MIA pathway: a key regulator of mitochondrial oxidative protein folding and biogenesis.Acc Chem Res. 2015 Aug 18;48(8):2191-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00150. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 26214018 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional roles of the conserved cysteine residues of the redox-regulated import receptor Mia40 in the intermembrane space of mitochondria.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 16;284(3):1353-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M805035200. Epub 2008 Nov 14. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19011240
-
The N-terminal shuttle domain of Erv1 determines the affinity for Mia40 and mediates electron transfer to the catalytic Erv1 core in yeast mitochondria.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010 Nov 1;13(9):1327-39. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3200. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010. PMID: 20367271
-
A disulfide relay system in mitochondria.Cell. 2005 Jul 1;121(7):965-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.019. Cell. 2005. PMID: 15989945 Review.
-
Structural basis for the disulfide relay system in the mitochondrial intermembrane space.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010 Nov 1;13(9):1359-73. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3099. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010. PMID: 20136511 Review.
Cited by
-
The C-terminal region of the oxidoreductase MIA40 stabilizes its cytosolic precursor during mitochondrial import.BMC Biol. 2020 Aug 6;18(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12915-020-00824-1. BMC Biol. 2020. PMID: 32762682 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting and import mechanism of coiled-coil helix coiled-coil helix domain-containing protein 3 (ChChd3) into the mitochondrial intermembrane space.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 16;287(47):39480-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.387696. Epub 2012 Sep 27. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23019327 Free PMC article.
-
The mitochondrial disulfide relay system: roles in oxidative protein folding and beyond.Int J Cell Biol. 2013;2013:742923. doi: 10.1155/2013/742923. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Int J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24348563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction with the cysteine-free protein HAX1 expands the substrate specificity and function of MIA40 beyond protein oxidation.FEBS J. 2024 Dec;291(24):5506-5522. doi: 10.1111/febs.17328. Epub 2024 Nov 20. FEBS J. 2024. PMID: 39564806 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial proteins: from biogenesis to functional networks.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019 May;20(5):267-284. doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0092-0. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30626975 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baker M.J., Webb C.T., Stroud D.A., Palmer C.S., Frazier A.E., Guiard B., Chacinska A., Gulbis J.M., Ryan M.T. 2009. Structural and functional requirements for activity of the Tim9-Tim10 complex in mitochondrial protein import. Mol. Biol. Cell. 20:769–779 10.1091/mbc.E08-09-0903 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

