IKK phosphorylates Huntingtin and targets it for degradation by the proteasome and lysosome
- PMID: 20026656
- PMCID: PMC2806289
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200909067
IKK phosphorylates Huntingtin and targets it for degradation by the proteasome and lysosome
Abstract
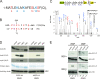
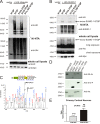
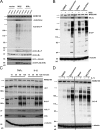
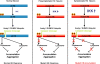
Expansion of the polyglutamine repeat within the protein Huntingtin (Htt) causes Huntington's disease, a neurodegenerative disease associated with aging and the accumulation of mutant Htt in diseased neurons. Understanding the mechanisms that influence Htt cellular degradation may target treatments designed to activate mutant Htt clearance pathways. We find that Htt is phosphorylated by the inflammatory kinase IKK, enhancing its normal clearance by the proteasome and lysosome. Phosphorylation of Htt regulates additional post-translational modifications, including Htt ubiquitination, SUMOylation, and acetylation, and increases Htt nuclear localization, cleavage, and clearance mediated by lysosomal-associated membrane protein 2A and Hsc70. We propose that IKK activates mutant Htt clearance until an age-related loss of proteasome/lysosome function promotes accumulation of toxic post-translationally modified mutant Htt. Thus, IKK activation may modulate mutant Htt neurotoxicity depending on the cell's ability to degrade the modified species.
Figures




References
-
- Aiken C.T., Steffan J.S., Guerrero C.M., Khashwji H., Lukacsovich T., Simmons D., Purcell J.M., Menhaji K., Zhu Y.Z., Green K., et al. 2009. Phosphorylation of threonine 3: implications for Huntingtin aggregation and neurotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 284:29427–29436 10.1074/jbc.M109.013193 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Apostol B.L., Simmons D.A., Zuccato C., Illes K., Pallos J., Casale M., Conforti P., Ramos C., Roarke M., Kathuria S., et al. 2008. CEP-1347 reduces mutant huntingtin-associated neurotoxicity and restores BDNF levels in R6/2 mice. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 39:8–20 10.1016/j.mcn.2008.04.007 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2R01NS039074/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039074/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS043466/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS045283/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS043466/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM74830/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045191/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045283/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052789/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG022074/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD036081/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01NS045191/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM074830/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG031782/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 2P01AG022074/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM0731130/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS055298/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS055298/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS043466/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HD36081/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NS52789/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01AG031782/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

