PtdIns4P recognition by Vps74/GOLPH3 links PtdIns 4-kinase signaling to retrograde Golgi trafficking
- PMID: 20026658
- PMCID: PMC2806290
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200909063
PtdIns4P recognition by Vps74/GOLPH3 links PtdIns 4-kinase signaling to retrograde Golgi trafficking
Abstract
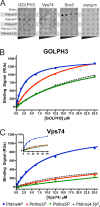
Targeting and retention of resident integral membrane proteins of the Golgi apparatus underly the function of the Golgi in glycoprotein and glycolipid processing and sorting. In yeast, steady-state Golgi localization of multiple mannosyltransferases requires recognition of their cytosolic domains by the peripheral Golgi membrane protein Vps74, an orthologue of human GOLPH3/GPP34/GMx33/MIDAS (mitochondrial DNA absence sensitive factor). We show that targeting of Vps74 and GOLPH3 to the Golgi apparatus requires ongoing synthesis of phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P) by the Pik1 PtdIns 4-kinase and that modulation of the levels and cellular location of PtdIns4P leads to mislocalization of these proteins. Vps74 and GOLPH3 bind specifically to PtdIns4P, and a sulfate ion in a crystal structure of GOLPH3 indicates a possible phosphoinositide-binding site that is conserved in Vps74. Alterations in this site abolish phosphoinositide binding in vitro and Vps74 function in vivo. These results implicate Pik1 signaling in retention of Golgi-resident proteins via Vps74 and show that GOLPH3 family proteins are effectors of Golgi PtdIns 4-kinases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Local control of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate signaling in the Golgi apparatus by Vps74 and Sac1 phosphoinositide phosphatase.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jul;23(13):2527-36. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-01-0077. Epub 2012 May 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22553352 Free PMC article.
-
Sac1-Vps74 structure reveals a mechanism to terminate phosphoinositide signaling in the Golgi apparatus.J Cell Biol. 2014 Aug 18;206(4):485-91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201404041. Epub 2014 Aug 11. J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25113029 Free PMC article.
-
GOLPH3 bridges phosphatidylinositol-4- phosphate and actomyosin to stretch and shape the Golgi to promote budding.Cell. 2009 Oct 16;139(2):337-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.052. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19837035 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination of Golgi functions by phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases.Trends Cell Biol. 2011 Feb;21(2):113-21. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.10.002. Epub 2010 Nov 4. Trends Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21282087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GOLPH3: a Golgi phosphatidylinositol(4)phosphate effector that directs vesicle trafficking and drives cancer.J Lipid Res. 2019 Feb;60(2):269-275. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R088328. Epub 2018 Sep 28. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 30266835 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of membrane curvature by proteins involved in Golgi trafficking.Adv Biol Regul. 2020 Jan;75:100661. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2019.100661. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Adv Biol Regul. 2020. PMID: 31668661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of protein retention in the Golgi.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Aug 1;3(8):a005264. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a005264. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 21525512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sorting of secretory proteins at the trans-Golgi network by human TGN46.Elife. 2024 Mar 11;12:RP91708. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91708. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38466628 Free PMC article.
-
GOLPH3 and GOLPH3L maintain Golgi localization of LYSET and a functional mannose 6-phosphate transport pathway.EMBO J. 2024 Dec;43(24):6264-6290. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00305-z. Epub 2024 Nov 25. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 39587297 Free PMC article.
-
Arf1 directly recruits the Pik1-Frq1 PI4K complex to regulate the final stages of Golgi maturation.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 May 1;32(10):1064-1080. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-02-0069. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33788598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bravo J., Karathanassis D., Pacold C.M., Pacold M.E., Ellson C.D., Anderson K.E., Butler P.J., Lavenir I., Perisic O., Hawkins P.T., et al. 2001. The crystal structure of the PX domain from p40(phox) bound to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate. Mol. Cell. 8:829–839 10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00372-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brunger A.T., Adams P.D., Clore G.M., DeLano W.L., Gros P., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., Jiang J.S., Kuszewski J., Nilges M., Pannu N.S., et al. 1998. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 54:905–921 - PubMed
-
- Collaborative Computational Project Number 4 1994. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallization. Acta. Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 50:760–763 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

