Antigen-specific suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by a novel bifunctional peptide inhibitor: structure optimization and pharmacokinetics
- PMID: 20026673
- PMCID: PMC2835440
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.161109
Antigen-specific suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by a novel bifunctional peptide inhibitor: structure optimization and pharmacokinetics
Abstract
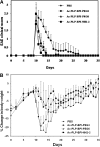
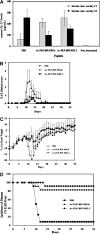
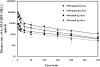
The objective of this study was to optimize the in vivo activity of proteolipid protein (PLP)-bifunctional peptide inhibitor (BPI) molecule to suppress experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in SJL/J mice and evaluate pharmacokinetic profiles of PLP-BPI. PLP-BPI is constructed via conjugation of myelin PLP(139-151) with CD11a(237-246)-derived peptide (LABL) via a spacer. The hypothesis is that PLP-BPI binds simultaneously to major histocompatibility complex-II and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on the antigen-presenting cell (APC) and inhibits the formation of the immunological synapse during T-cell and APC interactions. In this study, the structure of BPI was modified by varying the spacer and was evaluated in the EAE model. Intravenous injections of BPI derivatives inhibited the onset, severity, and incidence of EAE more effectively and induced a lower incidence of anaphylaxis than that produced by unmodified PLP-BPI. As anticipated, production of interleukin-17, a proinflammatory cytokine commonly found in elevated levels among multiple sclerosis (MS) patients, was significantly lower in Ac-PLP-BPI-PEG6- or Ac-PLP-BPI-NH(2)-2-treated mice than in phosphate-buffered saline-treated mice. These results suggest that BPI-type molecules can be modified to achieve more efficient and better tolerated BPI-based derivatives for the treatment of MS.
Figures

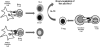
Similar articles
-
Antigen-specific suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by a novel bifunctional peptide inhibitor.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Aug;322(2):879-86. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.123257. Epub 2007 May 23. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17522343
-
Prophylactic and therapeutic suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by a novel bifunctional peptide inhibitor.Clin Immunol. 2008 Oct;129(1):69-79. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2008.06.002. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18676182 Free PMC article.
-
Immune response to controlled release of immunomodulating peptides in a murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model.J Control Release. 2010 Jan 25;141(2):145-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.09.002. Epub 2009 Sep 12. J Control Release. 2010. PMID: 19748537 Free PMC article.
-
Controlling immune response and demyelination using highly potent bifunctional peptide inhibitors in the suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2013 Apr;172(1):23-36. doi: 10.1111/cei.12029. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23480182 Free PMC article.
-
T cell response in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE): role of self and cross-reactive antigens in shaping, tuning, and regulating the autopathogenic T cell repertoire.Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:101-23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.081701.141316. Epub 2001 Oct 4. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11861599 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of EAE and prevention of blood-brain barrier breakdown after vaccination with novel bifunctional peptide inhibitor.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Mar;62(4):1874-81. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.12.013. Epub 2011 Dec 17. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22210333 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Tolerance Induction against Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) Using A New PLP-B7AP Conjugate that Simultaneously Targets B7/CD28 Costimulatory Signal and TCR/MHC-II Signal.J Mult Scler (Foster City). 2015 Dec;2(1):1000131. doi: 10.4172/2376-0389.1000131. J Mult Scler (Foster City). 2015. PMID: 26140285 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic acid graft polymers displaying peptide antigen modulate dendritic cell response in vitro.Mol Pharm. 2014 Jan 6;11(1):367-73. doi: 10.1021/mp4003909. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Mol Pharm. 2014. PMID: 24283935 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Administration of Soluble Antigen Arrays Is Superior to Antigen in Treatment of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.J Pharm Sci. 2017 Nov;106(11):3293-3302. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2017.06.008. Epub 2017 Jun 15. J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 28625726 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine-like controlled-release delivery of an immunomodulating peptide to treat experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Mol Pharm. 2012 Apr 2;9(4):979-85. doi: 10.1021/mp200614q. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Mol Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22375937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander C, Kay AB, Larche M. (2002) Peptide-based vaccines in the treatment of specific allergy. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 1:353–361 - PubMed
-
- Bielekova B, Goodwin B, Richert N, Cortese I, Kondo T, Afshar G, Gran B, Eaton J, Antel J, Frank JA, et al. (2000) Encephalitogenic potential of the myelin basic protein peptide (amino acids 83–99) in multiple sclerosis: results of a phase II clinical trial with an altered peptide ligand. Nat Med 6:1167–1175 - PubMed
-
- Bromley SK, Burack WR, Johnson KG, Somersalo K, Sims TN, Sumen C, Davis MM, Shaw AS, Allen PM, Dustin ML. (2001) The immunological synapse. Annu Rev Immunol 19:375–396 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

