Constitutive activation of Wnt signaling favors generation of memory CD8 T cells
- PMID: 20026746
- PMCID: PMC2809813
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901199
Constitutive activation of Wnt signaling favors generation of memory CD8 T cells
Abstract
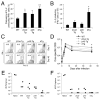
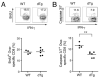
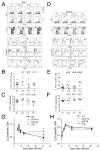
T cell factor-1 (TCF-1) and lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1, the effector transcription factors of the canonical Wnt pathway, are known to be critical for normal thymocyte development. However, it is largely unknown if it has a role in regulating mature T cell activation and T cell-mediated immune responses. In this study, we demonstrate that, like IL-7Ralpha and CD62L, TCF-1 and lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 exhibit dynamic expression changes during T cell responses, being highly expressed in naive T cells, downregulated in effector T cells, and upregulated again in memory T cells. Enforced expression of a p45 TCF-1 isoform limited the expansion of Ag-specific CD8 T cells in response to Listeria monocytogenes infection. However, when the p45 transgene was coupled with ectopic expression of stabilized beta-catenin, more Ag-specific memory CD8 T cells were generated, with enhanced ability to produce IL-2. Moreover, these memory CD8 T cells expanded to a larger number of secondary effectors and cleared bacteria faster when the immunized mice were rechallenged with virulent L. monocytogenes. Furthermore, in response to vaccinia virus or lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection, more Ag-specific memory CD8 T cells were generated in the presence of p45 and stabilized beta-catenin transgenes. Although activated Wnt signaling also resulted in larger numbers of Ag-specific memory CD4 T cells, their functional attributes and expansion after the secondary infection were not improved. Thus, constitutive activation of the canonical Wnt pathway favors memory CD8 T cell formation during initial immunization, resulting in enhanced immunity upon second encounter with the same pathogen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
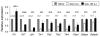


Similar articles
-
Essential role of the Wnt pathway effector Tcf-1 for the establishment of functional CD8 T cell memory.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 May 25;107(21):9777-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914127107. Epub 2010 May 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20457902 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting edge: generation of memory precursors and functional memory CD8+ T cells depends on T cell factor-1 and lymphoid enhancer-binding factor-1.J Immunol. 2012 Sep 15;189(6):2722-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201150. Epub 2012 Aug 8. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22875805 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive expression of IL-7 receptor alpha does not support increased expansion or prevent contraction of antigen-specific CD4 or CD8 T cells following Listeria monocytogenes infection.J Immunol. 2008 Mar 1;180(5):2855-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.5.2855. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18292507
-
Memory CD8+ T cell differentiation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Jan;1183:251-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05126.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20146720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TCF1 and beta-catenin regulate T cell development and function.Immunol Res. 2010 Jul;47(1-3):45-55. doi: 10.1007/s12026-009-8137-2. Immunol Res. 2010. PMID: 20082155 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The immunological synapse: the gateway to the HIV reservoir.Immunol Rev. 2013 Jul;254(1):305-25. doi: 10.1111/imr.12080. Immunol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23772628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue-resident memory T cells and their biological characteristics in the recurrence of inflammatory skin disorders.Cell Mol Immunol. 2020 Jan;17(1):64-75. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0291-4. Epub 2019 Oct 8. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31595056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential role of the Wnt pathway effector Tcf-1 for the establishment of functional CD8 T cell memory.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 May 25;107(21):9777-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914127107. Epub 2010 May 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20457902 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro-Generated Tc17 Cells Present a Memory Phenotype and Serve As a Reservoir of Tc1 Cells In Vivo.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 8;9:209. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00209. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29472932 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Aging and Immunotherapy in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 29;22(13):7016. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137016. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34209842 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harty JT, Badovinac VP. Shaping and reshaping CD8+ T-cell memory. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:107–119. - PubMed
-
- Seder RA, Ahmed R. Similarities and differences in CD4+ and CD8+ effector and memory T cell generation. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:835–842. - PubMed
-
- Badovinac VP, Porter BB, Harty JT. Programmed contraction of CD8(+) T cells after infection. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:619–626. - PubMed
-
- Berzofsky JA, Ahlers JD, Belyakov IM. Strategies for designing and optimizing new generation vaccines. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:209–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI050073/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI083286/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI059752/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI077504/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI183286/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI042767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI077504/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI046653/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI042767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL095540/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI083286/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI042767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI050073/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI046653/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI042767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI059752/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095540/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

