Identification of human GnIH homologs, RFRP-1 and RFRP-3, and the cognate receptor, GPR147 in the human hypothalamic pituitary axis
- PMID: 20027225
- PMCID: PMC2791420
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008400
Identification of human GnIH homologs, RFRP-1 and RFRP-3, and the cognate receptor, GPR147 in the human hypothalamic pituitary axis
Abstract
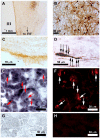
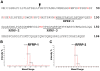
The existence of a hypothalamic gonadotropin-inhibiting system has been elusive. A neuropeptide named gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH, SIKPSAYLPLRF-NH(2)) which directly inhibits gonadotropin synthesis and release from the pituitary was recently identified in quail hypothalamus. Here we identify GnIH homologs in the human hypothalamus and characterize their distribution and biological activity. GnIH homologs were isolated from the human hypothalamus by immunoaffinity purification, and then identified as MPHSFANLPLRF-NH(2) (human RFRP-1) and VPNLPQRF-NH(2) (human RFRP-3) by mass spectrometry. Immunocytochemistry revealed GnIH-immunoreactive neuronal cell bodies in the dorsomedial region of the hypothalamus with axonal projections to GnRH neurons in the preoptic area as well as to the median eminence. RT-PCR and subsequent DNA sequencing of the PCR products identified human GnIH receptor (GPR147) mRNA expression in the hypothalamus as well as in the pituitary. In situ hybridization further identified the expression of GPR147 mRNA in luteinizing hormone producing cells (gonadotropes). Human RFRP-3 has recently been shown to be a potent inhibitor of gonadotropin secretion in cultured sheep pituitary cells by inhibiting Ca(2+) mobilization. It also directly modulates GnRH neuron firing. The identification of two forms of GnIH (RFRP-1 and RFRP-3) in the human hypothalamus which targets human GnRH neurons and gonadotropes and potently inhibit gonadotropin in sheep models provides a new paradigm for the regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis in man and a novel means for manipulating reproductive functions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucocorticoid receptor-mediated regulation of Rfrp (GnIH) and Gpr147 (GnIH-R) synthesis in immortalized hypothalamic neurons.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 Mar 25;384(1-2):23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.12.015. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24412804
-
Developmental changes in the mammalian gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH) ortholog RFamide-related peptide (RFRP) and its cognate receptor GPR147 in the rat hypothalamus.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2012 Feb;30(1):31-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2011.10.003. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22064075
-
The control of reproductive physiology and behavior by gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone.Integr Comp Biol. 2008 Nov;48(5):560-9. doi: 10.1093/icb/icn019. Epub 2008 Apr 27. Integr Comp Biol. 2008. PMID: 20607134 Free PMC article.
-
Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH), GnIH receptor and cell signaling.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2013 Sep 1;190:10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2013.02.030. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23499786 Review.
-
Central and direct regulation of testicular activity by gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone and its receptor.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Jan 27;5:8. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00008. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 24478760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glucocorticoids and Their Receptor Isoforms: Roles in Female Reproduction, Pregnancy, and Foetal Development.Biology (Basel). 2023 Aug 9;12(8):1104. doi: 10.3390/biology12081104. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37626990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arg-Phe-amide-related peptides influence gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons.Neural Regen Res. 2013 Jun 25;8(18):1714-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.18.009. Neural Regen Res. 2013. PMID: 25206468 Free PMC article.
-
The Arg-Phe-amide peptide 26RFa/glutamine RF-amide peptide and its receptor: IUPHAR Review 24.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;174(20):3573-3607. doi: 10.1111/bph.13907. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28613414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Regulation by the Hypothalamic Neuropeptide, Gonadotropin-Inhibitory Hormone at Both the Central and Peripheral Levels.Cells. 2025 Feb 12;14(4):267. doi: 10.3390/cells14040267. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39996740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basic biology is not just "for the birds": how avian studies have informed us about vertebrate reproduction.F S Rep. 2025 Apr 15;6(Suppl 1):7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.xfre.2024.12.007. eCollection 2025 Apr. F S Rep. 2025. PMID: 40487323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsuo H, Baba Y, Nair RM, Arimura A, Schally AV. Structure of the porcine LH- and FSH-releasing hormone. I. The proposed amino acid sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971;43:1334–1339. - PubMed
-
- King JA, Millar RP. Structure of chicken hypothalamic luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. I. Structural determination on partially purified material. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:10722–10728. - PubMed
-
- King JA, Millar RP. Structure of chicken hypothalamic luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. II. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:10729–10732. - PubMed
-
- Miyamoto K, Hasegawa Y, Minegishi T, Nomura M, Takahashi Y, et al. 1982 Isolation and characterization of chicken hypothalamic luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 107:820–827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

