The ability of rodent islet amyloid polypeptide to inhibit amyloid formation by human islet amyloid polypeptide has important implications for the mechanism of amyloid formation and the design of inhibitors
- PMID: 20028124
- PMCID: PMC2882292
- DOI: 10.1021/bi901751b
The ability of rodent islet amyloid polypeptide to inhibit amyloid formation by human islet amyloid polypeptide has important implications for the mechanism of amyloid formation and the design of inhibitors
Abstract
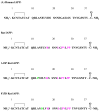
Islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) is a 37-residue polypeptide hormone that is responsible for islet amyloid formation in type II diabetes. Human IAPP is extremely amyloidogenic, while rat IAPP and mouse IAPP do not form amyloid in vitro or in vivo. Rat IAPP and mouse IAPP have identical primary sequences, but differ from the human polypeptide at six positions, five of which are localized between residues 20 and 29. The ability of rat IAPP to inhibit amyloid formation by human IAPP was tested, and the rat peptide was found to be an effective inhibitor. Thioflavin-T fluorescence-monitored kinetic experiments, transmission electron microscopy, and circular dichroism showed that rat IAPP lengthened the lag phase for amyloid formation by human IAPP, slowed the growth rate, reduced the amount of amyloid fibrils produced in a dose-dependent manner, and altered the morphology of the fibrils. The inhibition of human IAPP amyloid formation by rat IAPP can be rationalized by a model that postulates formation of an early helical intermediate during amyloid formation where the helical region is localized to the N-terminal region of IAPP. The model predicts that proline mutations in the putative helical region should lead to ineffective inhibitors as should mutations that alter the peptide-peptide interaction interface. We confirmed this by testing the ability of A13P and F15D point mutants of rat IAPP to inhibit amyloid formation by human IAPP. Both these mutants were noticeably less effective inhibitors than wild-type rat IAPP. The implications for inhibitor design are discussed.
Figures







References
-
- Chiti F, Dobson CM. Protein misfolding, functional amyloid, and human disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:333–366. - PubMed
-
- Sipe JD. Amyloidosis. Crit Rev Cl Lab Sci. 1994;31:325–354. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Cell biology of protein misfolding: The examples of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6:1054–1061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

