Co-infection by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and human T cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1): does immune activation lead to a faster progression to AIDS?
- PMID: 20028500
- PMCID: PMC2813852
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-9-211
Co-infection by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and human T cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1): does immune activation lead to a faster progression to AIDS?
Abstract
Background: Recent data have shown that HTLV-1 is prevalent among HIV positive patients in Mozambique, although the impact of HTLV-1 infection on HIV disease progression remains controversial. Our aim was to determine the phenotypic profile of T lymphocytes subsets among Mozambican patients co-infected by HIV and HTLV-1.
Methods: We enrolled 29 patients co-infected by HTLV-1 and HIV (co-infected), 59 patients mono-infected by HIV (HIV) and 16 healthy controls (HC), respectively.For phenotypic analysis, cells were stained with the following fluorochrome-labeled anti-human monoclonal antibodies CD4-APC, CD8-PerCP, CD25-PE, CD62L-FITC, CD45RA-FITC. CD45RO-PE, CD38-PE; being analysed by four-colour flow cytometry.
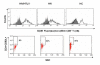
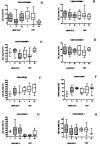
Results: We initially found that CD4+ T cell counts were significantly higher in co-infected, as compared to HIV groups. Moreover, CD4+ T Lymphocytes from co-infected patients presented significantly higher levels of CD45RO and CD25, but lower levels of CD45RA and CD62L, strongly indicating that CD4+ T cells are more activated under HTLV-1 plus HIV co-infection.
Conclusion: Our data indicate that HTLV-1/HIV co-infected patients progress with higher CD4+ T cell counts and higher levels of activation markers. In this context, it is conceivable that in co-infected individuals, these higher levels of activation may account for a faster progression to AIDS.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Loss of correlation between HIV viral load and CD4+ T-cell counts in HIV/HTLV-1 co-infection in treatment naive Mozambican patients.Int J STD AIDS. 2009 Dec;20(12):863-8. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2008.008401. Int J STD AIDS. 2009. PMID: 19948902
-
CD4(+)CD25(High) Treg cells in HIV/HTLV co-infected patients with neuropathy: high expression of Alpha4 integrin and lower expression of Foxp3 transcription factor.BMC Immunol. 2015 Sep 2;16:52. doi: 10.1186/s12865-015-0116-x. BMC Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26329520 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of absolute CD4+ count in predicting co-infection with human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 in antiretroviral-naive HIV-infected patients.Int J STD AIDS. 2012 Oct;23(10):717-23. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2012.011446. Int J STD AIDS. 2012. PMID: 23104746
-
Molecular and cellular interactions of HIV-1/HTLV coinfection and impact on AIDS progression.AIDS Rev. 2007 Jul-Sep;9(3):140-9. AIDS Rev. 2007. PMID: 17982939 Review.
-
Human retroviruses after 20 years: a perspective from the past and prospects for their future control.Immunol Rev. 2002 Jul;185:236-65. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2002.18520.x. Immunol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12190935 Review.
Cited by
-
Human T-Lymphotropic virus type 1 and human immunodeficiency virus co-infection in rural Gabon.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 22;17(7):e0271320. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271320. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35867643 Free PMC article.
-
HTLV-2 Encoded Antisense Protein APH-2 Suppresses HIV-1 Replication.Viruses. 2021 Jul 23;13(8):1432. doi: 10.3390/v13081432. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34452297 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of CC-chemokines with antiviral function in macrophages by the human T lymphotropic virus type 2 transactivating protein, Tax2.Viral Immunol. 2013 Feb;26(1):3-12. doi: 10.1089/vim.2012.0060. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Viral Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23286582 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of Epigenetic Silencing Allows Robust HIV-1 Replication in the Absence of Integrase Function.mBio. 2020 Jun 2;11(3):e01038-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01038-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32487757 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of WHO criteria for identifying ART treatment failure in Vietnam from 2007 to 2011.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 6;12(9):e0182688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182688. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28877173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 2007. JUNPoHAUaWHOW. AIDS epidemic update: December 2007. AIDS epidemic update: December 2007. 2007.
-
- Hattori T, Koito A, Takatsuki K, Ikematsu S, Matsuda J, Mori H, Fukui M, Akashi K, Matsumoto K. Frequent infection with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I in patients with AIDS but not in carriers of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(3):272–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

