Antigen-specific influence of GM/KM allotypes on IgG isotypes and association of GM allotypes with susceptibility to Plasmodium falciparum malaria
- PMID: 20028548
- PMCID: PMC2805690
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-8-306
Antigen-specific influence of GM/KM allotypes on IgG isotypes and association of GM allotypes with susceptibility to Plasmodium falciparum malaria
Abstract
Background: Plasmodium falciparum malaria is a complex disease in which genetic and environmental factors influence susceptibility. IgG isotypes are in part genetically controlled, and GM/KM allotypes are believed to be involved in this control.
Methods: In this study, 216 individuals from Daraweesh, an area of seasonal malaria transmission in Sudan, were followed for nine years for malaria infection. Total IgG and IgG isotypes against four malaria antigens, MSP2-3D7, MSP2-FC27, AMA1, and Pf332-C231 were measured in plasma obtained from the cohort at the end of the study, during the dry malaria-free period. The GM/KM allotypes of the donors were determined.
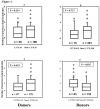
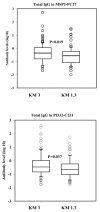
Results: The GM 1,17 5,13,14,6 phenotype was associated with a higher incidence of malaria compared with the non-1,17 5,13,14,6 phenotypes (P = 0.037). Paradoxically, the carriers of the GM 1,17 5,13,14,6 phenotype had significantly higher baseline levels of total IgG and non-cytophilic IgG isotypes as compared to non-carriers. The KM allotypes influence on IgG isotypes level was limited. Finally, the differences in the baseline concentrations of total IgG and IgG isotypes between the different GK/KM phenotype carriers were antigen-dependent.
Discussion: The results show that GM but not KM allotypes appeared to influence host susceptibility to uncomplicated malaria as well as the antibody profile of the donors, and the carriers of the GM 1,17 5,13,14,6 phenotype were the most susceptible
Conclusions: The GM allotypes have significant influence on susceptibility to uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria and antigen-dependent influence on total IgG and IgG subclasses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Age-dependent association between IgG2 and IgG3 subclasses to Pf332-C231 antigen and protection from malaria, and induction of protective antibodies by sub-patent malaria infections, in Daraweesh.Vaccine. 2010 Feb 17;28(7):1732-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.12.018. Epub 2009 Dec 28. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 20036751
-
Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface antigen-specific cytophilic IgG and control of malaria infection in a Beninese birth cohort.Malar J. 2019 Jun 11;18(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2831-x. Malar J. 2019. PMID: 31185998 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of multi-locus polymorphisms in an immune network with susceptibility to uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Daraweesh village, Eastern Sudan.Infect Genet Evol. 2011 Oct;11(7):1674-81. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2011.06.015. Epub 2011 Jun 26. Infect Genet Evol. 2011. PMID: 21729768
-
Pattern of pre-existing IgG subclass responses to a panel of asexual stage malaria antigens reported during the lengthy dry season in Daraweesh, Sudan.Scand J Immunol. 2011 Oct;74(4):390-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2011.02585.x. Scand J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21645028
-
Humoral responses to Plasmodium falciparum blood-stage antigens and association with incidence of clinical malaria in children living in an area of seasonal malaria transmission in Burkina Faso, West Africa.Infect Immun. 2008 Feb;76(2):759-66. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01147-07. Epub 2007 Dec 10. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18070896 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Susceptibility to Plasmodium falciparum Malaria: Influence of Combined Polymorphisms of IgG3 Gm Allotypes and Fc Gamma Receptors IIA, IIIA, and IIIB.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 23;11:608016. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.608016. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33424858 Free PMC article.
-
Association between immunoglobulin GM and KM genotypes and placental malaria in HIV-1 negative and positive women in western Kenya.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53948. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053948. Epub 2013 Jan 11. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23326546 Free PMC article.
-
GM Allotypes and COVID-19. A Pilot Study Performed on Sicilian Patients.Transl Med UniSa. 2022 Dec 27;24(2):26-29. doi: 10.37825/2239-9747.1039. eCollection 2022. Transl Med UniSa. 2022. PMID: 37476201 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin GM 3 23 5,13,14 phenotype is strongly associated with IgG1 antibody responses to Plasmodium vivax vaccine candidate antigens PvMSP1-19 and PvAMA-1.Malar J. 2010 Aug 9;9:229. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-9-229. Malar J. 2010. PMID: 20696056 Free PMC article.
-
Fc Proteoforms of ACPA IgG Discriminate Autoimmune Responses in Plasma and Synovial Fluid of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and Associate with Disease Activity.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(15):e2408769. doi: 10.1002/advs.202408769. Epub 2025 Feb 22. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39985219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roussilhon C, Oeuvray C, MÜller-Graf C, Tall A, Rogier C, Trape JF, Theisen M, Balde A, Pérignon JL, Druilhe P. Long-term clinical protection from falciparum malaria is strongly associated with IgG3 antibodies to merozoite surface protein 3. PLoS Med. 2007;13:e320. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040320. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lefranc MP, Lefranc G. Molecular genetics of immunoglobulin allotype expression. In The human IgG subclasses: Molecular analysis of structure function and regulation. Farouk Shakib Oxford; 1990. pp. 43–78.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

