c-Jun-NH2-kinase-1 inhibition leads to antitumor activity in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 20028751
- PMCID: PMC3716580
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1180
c-Jun-NH2-kinase-1 inhibition leads to antitumor activity in ovarian cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To show the functional, clinical, and biological significance of c-Jun-NH(2)-kinase (JNK)-1 in ovarian carcinoma.
Experimental design: Analysis of the impact of JNK on 116 epithelial ovarian cancers was conducted. The role of JNK in vitro and in experimental models of ovarian cancer was assessed. We studied the role of N-5-[4-(4-methyl piperazine methyl)-benzoylamido]-2-methylphenyl-4-[3-(4-methyl)-pyridyl]-2-pyrimidine amine (WBZ_4), a novel JNK inhibitor redesigned from imatinib based on targeting wrapping defects, in cell lines and in experimental models of ovarian cancer.
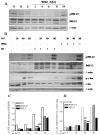
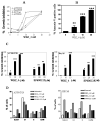
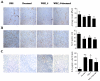
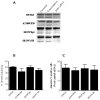
Results: We found a significant association of pJNK with progression-free survival in the 116 epithelial ovarian cancers obtained at primary debulking therapy. WBZ_4 led to cell growth inhibition and increased apoptosis in a dose-dependent fashion in four ovarian cancer cell lines. In vivo, whereas imatinib had no effect on tumor growth, WBZ_4 inhibited tumor growth in orthotopic murine models of ovarian cancer. The antitumor effect was further increased in combination with docetaxel. Silencing of JNK-1 with systemically administered siRNA led to significantly reduced tumor weights compared with nonsilencing siRNA controls, indicating that indeed the antitumor effects observed were due to JNK-1 inhibition.
Conclusions: These studies identify JNK-1 as an attractive therapeutic target in ovarian carcinoma and that the redesigned WBZ_4 compound should be considered for further clinical development.
Figures

References
-
- Davis RJ. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell. 2000;103:239–52. - PubMed
-
- Harper SJ, LoGrasso P. Signalling for survival and death in neurones: the role of stress-activated kinases, JNK and p38. Cellular signalling. 2001;13:299–310. - PubMed
-
- Chang L, Karin M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature. 2001;410:37–40. - PubMed
-
- Hibi M, Lin A, Smeal T, Minden A, Karin M. Identification of an oncoprotein- and UV-responsive protein kinase that binds and potentiates the c-Jun activation domain. Genes & development. 1993;7:2135–48. - PubMed
-
- Kyriakis JM, Banerjee P, Nikolakaki E, et al. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994;369:156–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

