Targeting the cyclin E-Cdk-2 complex represses lung cancer growth by triggering anaphase catastrophe
- PMID: 20028770
- PMCID: PMC2805048
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2151
Targeting the cyclin E-Cdk-2 complex represses lung cancer growth by triggering anaphase catastrophe
Abstract
Purpose: Cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdk) and their associated cyclins are targets for lung cancer therapy and chemoprevention given their frequent deregulation in lung carcinogenesis. This study uncovered previously unrecognized consequences of targeting the cyclin E-Cdk-2 complex in lung cancer.
Experimental design: Cyclin E, Cdk-1, and Cdk-2 were individually targeted for repression with siRNAs in lung cancer cell lines. Cdk-2 was also pharmacologically inhibited with the reversible kinase inhibitor seliciclib. Potential reversibility of seliciclib effects was assessed in washout experiments. Findings were extended to a large panel of cancer cell lines using a robotic-based platform. Consequences of cyclin E-Cdk-2 inhibition on chromosome stability and on in vivo tumorigenicity were explored as were effects of combining seliciclib with different taxanes in lung cancer cell lines.
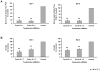
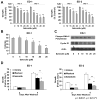
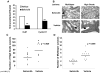
Results: Targeting the cyclin E-Cdk-2 complex, but not Cdk-1, resulted in marked growth inhibition through the induction of multipolar anaphases triggering apoptosis. Treatment with the Cdk-2 kinase inhibitor seliciclib reduced lung cancer formation in a murine syngeneic lung cancer model and decreased immunohistochemical detection of the proliferation markers Ki-67 and cyclin D1 in lung dysplasia spontaneously arising in a transgenic cyclin E-driven mouse model. Combining seliciclib with a taxane resulted in augmented growth inhibition and apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Pharmacogenomic analysis revealed that lung cancer cell lines with mutant ras were especially sensitive to seliciclib.
Conclusions: Induction of multipolar anaphases leading to anaphase catastrophe is a previously unrecognized mechanism engaged by targeting the cyclin E-Cdk-2 complex. This exerts substantial antineoplastic effects in the lung.
Figures



References
-
- Shapiro GI. Cyclin-dependent kinase pathways as targets for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1770–83. - PubMed
-
- Koff A, Giordano A, Desai D, et al. Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 1992;257:1689–94. - PubMed
-
- Freemantle SJ, Liu X, Feng Q, et al. Cyclin degradation for cancer therapy and chemoprevention. J Cell Biochem. 2007;102:869–77. - PubMed
-
- Harbour JW, Luo RX, Dei Santi A, Postigo AA, Dean DC. Cdk phosphorylation triggers sequential intramolecular interactions that progressively block Rb functions as cells move through G1. Cell. 1999;98:859–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

