QseC mediates Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium virulence in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 20028809
- PMCID: PMC2825943
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01038-09
QseC mediates Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium virulence in vitro and in vivo
Erratum in
- Infect Immun. 2010 Aug;78(8):3647
Abstract
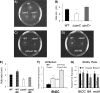
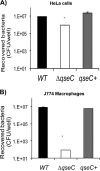
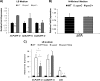
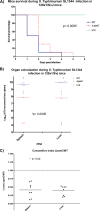
The autoinducer-3 (AI-3)/epinephrine (Epi)/norepinephrine (NE) interkingdom signaling system mediates chemical communication between bacteria and their mammalian hosts. The three signals are sensed by the QseC histidine kinase (HK) sensor. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is a pathogen that uses HKs to sense its environment and regulate virulence. Salmonella serovar Typhimurium invades epithelial cells and survives within macrophages. Invasion of epithelial cells is mediated by the type III secretion system (T3SS) encoded in Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1), while macrophage survival and systemic disease are mediated by the T3SS encoded in SPI-2. Here we show that QseC plays an important role in Salmonella serovar Typhimurium pathogenicity. A qseC mutant was impaired in flagellar motility, in invasion of epithelial cells, and in survival within macrophages and was attenuated for systemic infection in 129x1/SvJ mice. QseC acts globally, regulating expression of genes within SPI-1 and SPI-2 in vitro and in vivo (during infection of mice). Additionally, dopamine beta-hydroxylase knockout (Dbh(-)(/)(-)) mice that do not produce Epi or NE showed different susceptibility to Salmonella serovar Typhimurium infection than wild-type mice. These data suggest that the AI-3/Epi/NE signaling system is a key factor during Salmonella serovar Typhimurium pathogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Elucidation of the role of this interkingdom signaling system in Salmonella serovar Typhimurium should contribute to a better understanding of the complex interplay between the pathogen and the host during infection.
Figures



References
-
- Ader, R., N. Cohen, and D. Felten. 1995. Psychoneuroimmunology: interactions between the nervous system and the immune system. Lancet 345:99-103. - PubMed
-
- Arnett, C. D., J. Wright, and N. Zenker. 1978. Synthesis and adrenergic activity of benzimidazole bioisosteres of norepinephrine and isoproterenol. J. Med. Chem. 21:72-78. - PubMed
-
- Ashby, M. K. 2004. Survey of the number of two-component response regulator genes in the complete and annotated genome sequences of prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 231:277-281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

