Extracts of the rat tapeworm, Hymenolepis diminuta, suppress macrophage activation in vitro and alleviate chemically induced colitis in mice
- PMID: 20028812
- PMCID: PMC2825920
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01349-08
Extracts of the rat tapeworm, Hymenolepis diminuta, suppress macrophage activation in vitro and alleviate chemically induced colitis in mice
Abstract
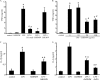
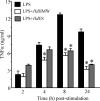
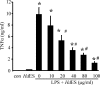
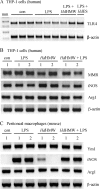
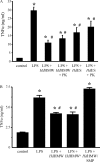
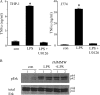
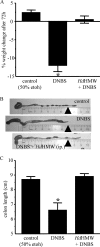
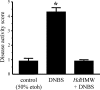
Analysis of parasite-host interactions can reveal the intricacies of immunity and identify ways to modulate immunopathological reactions. We assessed the ability of a phosphate-buffered saline-soluble extract of adult Hymenolepis diminuta to suppress macrophage (human THP-1 cell line, murine peritoneal macrophages) activity in vitro and the impact of treating mice with this extract on colitis induced by dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (DNBS). A high-molecular-mass fraction of adult H. diminuta (HdHMW) or excretory/secretory products reduced macrophage activation: lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and poly(I:C)-induced TNF-alpha and IL-6 were suppressed by HdHMW. The active component in the HdHMW extract was minimally sensitive to boiling and trypsin digestion, whereas the use of sodium metaperiodate, as a general deglycosylation strategy, indicated that the immunosuppressive effect of HdHMW was at least partially dependent on a glycan: treating the HdHMW with neuraminidase and alpha-mannosidase failed to inhibit its blockade of LPS-induced TNF-alpha production by THP-1 macrophages. Mice treated with DNBS developed colitis, as typified by wasting, shortening of the colon, macroscopic and microscopic tissue damage, and an inflammatory infiltrate. Mice cotreated with HdHMW (three intraperitoneal injections) displayed significantly less inflammatory disease, and this was accompanied by reduced TNF-alpha production and increased IL-10 and IL-4 production by mitogen-stimulated spleen cells. However, cotreatment of mice with neutralizing anti-IL-10 antibodies had only a minor impact on the anticolitic effect of the HdHMW. We speculate that purification of the immunosuppressive factor(s) from H. diminuta has the potential to lead to the development of novel immunomodulatory drugs to treat inflammatory disease.
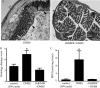
Figures
References
-
- Cliffe, L. J., N. E. Humphreys, T. E. Lane, C. S. Potten, C. Booth, and R. K. Grencis. 2005. Accelerated intestinal epithelial cell turnover: a new mechanism of parasite expulsion. Science 308:1463-1465. - PubMed
-
- Culley, F. J., A. Brown, D. M. Conroy, I. Sabroe, D. I. Pritchard, and T. J. Williams. 2000. Eotaxin is specifically cleaved by hookworm metalloproteases preventing its action in vitro and in vivo. J. Immunol. 165:6447-6453. - PubMed
-
- Deehan, M. R., M. M. Harnett, and W. Harnett. 1997. A filarial nematode secreted product differentially modulates expression and activation of protein kinase C isoforms in B lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 159:6105-6111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

