Early viral kinetics of telbivudine and entecavir: results of a 12-week randomized exploratory study with patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 20028815
- PMCID: PMC2826006
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01163-09
Early viral kinetics of telbivudine and entecavir: results of a 12-week randomized exploratory study with patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
We characterized the early viral kinetic profiles of telbivudine and entecavir and the effects of these potent nucleoside analogs on hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA and alanine aminotransferase levels in adults with hepatitis B e antigen-positive compensated chronic hepatitis B. Forty-four patients were enrolled in this open-label, parallel-group, multicenter study and randomized to receive telbivudine or entecavir for 12 weeks. Reductions in hepatitis B virus DNA and alanine aminotransferase levels from baseline to weeks 2, 4, 8, and 12 were assessed. Viral kinetic parameters, including viral clearance per day, loss of infected cells per day, and efficiency of inhibition of viral production, were estimated by using a biphasic mathematical model. Statistical analyses were limited to descriptive analyses. The 2 treatment groups achieved similar reductions in HBV DNA and alanine aminotransferase levels. Mean reductions in levels of hepatitis B virus DNA at week 12 were 6.6 +/- 1.6 and 6.5 +/- 1.5 log(10) copies/ml for the telbivudine- and entecavir-treated patients, respectively. There were no significant differences between groups in values for mean viral clearance per day, mean loss of infected cells per day, or efficiency of blocking viral production. The safety profiles for both medications were favorable. During the first 12 weeks of treatment, telbivudine and entecavir demonstrated similar antiviral potencies, resulting in a rapid and profound suppression of serum hepatitis B virus DNA and reduction of alanine aminotransferase levels. No differences in the effects of these 2 agents on early viral kinetics were observed. Both medications were well tolerated.
Figures

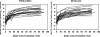

Similar articles
-
Telbivudine: a review of its use in compensated chronic hepatitis B.Drugs. 2010 Oct 1;70(14):1857-83. doi: 10.2165/11204330-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20836578 Review.
-
A 24-week, parallel-group, open-label, randomized clinical trial comparing the early antiviral efficacy of telbivudine and entecavir in the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection in adult Chinese patients.Clin Ther. 2010 Apr;32(4):649-58. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.04.001. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20435234 Clinical Trial.
-
A comparison of telbivudine and entecavir for chronic hepatitis B in real-world clinical practice.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012 Mar;67(3):696-9. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr495. Epub 2011 Dec 15. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22174039
-
[Short-term results of telbivudine versus entecavir treatments in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients in China].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2008 Sep;16(9):641-5. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18822200 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Effects of telbivudine and entecavir for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Nov 21;18(43):6290-301. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6290. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23180951 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and Safety of Telbivudine Compared to Entecavir Among HBeAg+ Chronic Hepatitis B Patients: a Meta-Analysis Study.Hepat Mon. 2013 May 23;13(6):e7862. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.7862. eCollection 2013. Hepat Mon. 2013. PMID: 24032045 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis for Assessing Adverse Effects of Anti-hepatitis B Drugs.Clin Drug Investig. 2019 Sep;39(9):835-846. doi: 10.1007/s40261-019-00802-8. Clin Drug Investig. 2019. PMID: 31228017
-
Two-year results of a randomized, phase III comparative trial of telbivudine versus lamivudine in Chinese patients.Hepatol Int. 2014 Jan;8(1):72-82. doi: 10.1007/s12072-013-9488-2. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Hepatol Int. 2014. PMID: 26202408
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Optimal treatment strategies based on liver segmentation and functional hepatic reserve.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2015 Nov-Dec;20(6):417-24. doi: 10.1016/j.rpor.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2015. PMID: 26696781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telbivudine: a review of its use in compensated chronic hepatitis B.Drugs. 2010 Oct 1;70(14):1857-83. doi: 10.2165/11204330-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20836578 Review.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2008. Hepatitis B FAQs for health professionals. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA. http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/HBV/HBVfaq.htm#overview.
-
- Chan, H. L., E. J. Heathcote, P. Marcellin, C. L. Lai, M. Cho, Y. M. Moon, Y. C. Chao, R. P. Myers, G. Y. Minuk, L. Jeffers, W. Sievert, N. Bzowej, G. Harb, R. Kaiser, X. J. Qiao, and N. A. Brown on behalf of the 018 Study Group. 2007. Treatment of hepatitis B e antigen positive chronic hepatitis with telbivudine or adefovir: a randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 147:745-754. - PubMed
-
- Chang, T. T., R. G. Gish, R. de Man, A. Gadano, J. Sollano, Y. C. Chao, A. S. Lok, K. H. Han, Z. Goodman, J. Zhu, A. Cross, D. Dehertogh, R. Wilber, R. Colonno, and D. Apelian. 2006. A comparison of entecavir and lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. N. Engl. J. Med. 354:1001-1010. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C. J., H. I. Yang, J. Su, C. L. Jen, S. L. You, S. N. Lu, G. T. Huang, and U. H. Iloeje. 2006. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 295:65-73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

