Drosophila brain development: closing the gap between a macroarchitectural and microarchitectural approach
- PMID: 20028843
- PMCID: PMC3950651
- DOI: 10.1101/sqb.2009.74.037
Drosophila brain development: closing the gap between a macroarchitectural and microarchitectural approach
Abstract
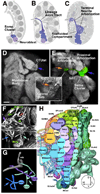
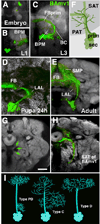
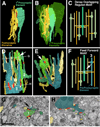
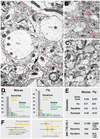
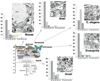
Neurobiologists address neural structure, development, and function at the level of "macrocircuits" (how different brain compartments are interconnected; what overall pattern of activity they produce) and at the level of "microcircuits" (how connectivity and physiology of individual neurons and their processes within a compartment determine the functional output of this compartment). Work in our lab aims at reconstructing the developing Drosophila brain at both levels. Macrocircuits can be approached conveniently by reconstructing the pattern of brain lineages, which form groups of neurons whose projections form cohesive fascicles interconnecting the compartments of the larval and adult brain. The reconstruction of microcircuits requires serial section electron microscopy, due to the small size of terminal neuronal processes and their synaptic contacts. Because of the amount of labor that traditionally comes with this approach, very little is known about microcircuitry in brains across the animal kingdom. Many of the problems of serial electron microscopy reconstruction are now solvable with digital image recording and specialized software for both image acquisition and postprocessing. In this chapter, we introduce our efforts to reconstruct the small Drosophila larval brain and discuss our results in light of the published data on neuropile ultrastructure in other animal taxa.
Figures


References
-
- Alon U. Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007;8:450–461. - PubMed
-
- Baas PW, Yu W. A composite model for establishing the microtubule arrays of the neuron. Mol. Neurobiol. 1996;12:145–161. - PubMed
-
- Braitenberg V, Schüz A. Cortex: Statistics and Geometry of Neuronal Connectivity. 2nd. Springer: Berlin Heidelberg; 1998.
-
- Brand AH, Perrimon N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 1993;118:401–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
