Regulatory T cell-mediated resolution of lung injury: identification of potential target genes via expression profiling
- PMID: 20028937
- PMCID: PMC2853901
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00131.2009
Regulatory T cell-mediated resolution of lung injury: identification of potential target genes via expression profiling
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Physiol Genomics. 2016 Dec 1;48(12):961. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.zh7-4153-corr.2016. Physiol Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27994048 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
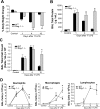
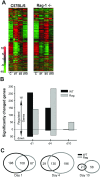
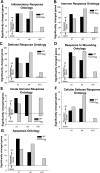
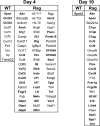
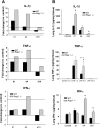
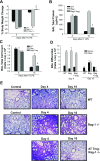
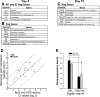
In animal models of acute lung injury (ALI), gene expression studies have focused on the acute phase of illness, with little emphasis on resolution. In this study, the acute phase of intratracheal lipopolysaccharide (IT LPS)-induced lung injury was similar in wild-type (WT) and recombinase-activating gene-1-deficient (Rag-1(-/-)) lymphocyte-deficient mice, but resolution was impaired and resolution-phase lung gene expression remained different from baseline only in Rag-1(-/-) mice. By focusing on groups of genes involved in similar biological processes (gene ontologies) pertinent to inflammation and the immune response, we identified 102 genes at days 4 and 10 after IT LPS with significantly different expression between WT and Rag-1(-/-) mice. After adoptive transfer of isolated CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) to Rag-1(-/-) mice at the time of IT LPS, resolution was similar to that in WT mice. Of the 102 genes distinctly changed in either WT or Rag-1(-/-) mice from our 7 gene ontologies, 19 genes reverted from the Rag-1(-/-) to the WT pattern of expression after adoptive transfer of Tregs, implicating those 19 genes in Treg-mediated resolution of ALI.
Figures
References
-
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 342: 1301–1308, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Altemeier WA, Matute-Bello G, Gharib SA, Glenny RW, Martin TR, Liles WC. Modulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced gene transcription and promotion of lung injury by mechanical ventilation. J Immunol 175: 3369–3376, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Brass DM, Yang IV, Kennedy MP, Whitehead GS, Rutledge H, Burch LH, Schwartz DA. Fibroproliferation in LPS-induced airway remodeling and bleomycin-induced fibrosis share common patterns of gene expression. Immunogenetics 60: 353–369, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Cheadle C, Cho-Chung YS, Becker KG, Vawter MP. Application of z-score transformation to Affymetrix data. Appl Bioinformatics 2: 209–217, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

