Activation of the Ran GTPase is subject to growth factor regulation and can give rise to cellular transformation
- PMID: 20028979
- PMCID: PMC2820807
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.071886
Activation of the Ran GTPase is subject to growth factor regulation and can give rise to cellular transformation
Abstract
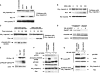
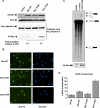
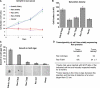
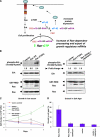
Although the small GTPase Ran is best known for its roles in nucleocytoplasmic transport, mitotic spindle assembly, and nuclear envelope formation, recent studies have demonstrated the overexpression of Ran in multiple tumor types and that its expression is correlated with a poor patient prognosis, providing evidence for the importance of this GTPase in cell growth regulation. Here we show that Ran is subject to growth factor regulation by demonstrating that it is activated in a serum-dependent manner in human breast cancer cells and, in particular, in response to heregulin, a growth factor that activates the Neu/ErbB2 tyrosine kinase. The heregulin-dependent activation of Ran requires mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) and stimulates the capped RNA binding capability of the cap-binding complex in the nucleus, thus influencing gene expression at the level of mRNA processing. We further demonstrate that the excessive activation of Ran has important consequences for cell growth by showing that a novel, activated Ran mutant is sufficient to transform NIH-3T3 cells in an mTOR- and epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent manner and that Ran-transformed cells form tumors in mice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of a novel activated Ran GTPase mutant and its ability to induce cellular transformation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 20;287(30):24955-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.306514. Epub 2012 Jun 7. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22679017 Free PMC article.
-
HER2 (neu) signaling increases the rate of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) synthesis: novel mechanism for HIF-1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jun;21(12):3995-4004. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.12.3995-4004.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11359907 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics identification of nuclear Ran GTPase as an inhibitor of human VRK1 and VRK2 (vaccinia-related kinase) activities.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008 Nov;7(11):2199-214. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M700586-MCP200. Epub 2008 Jul 9. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008. PMID: 18617507 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic functions of the Ran GTPase network: the importance of being in the right place at the right time.Cell Cycle. 2004 Mar;3(3):305-13. Epub 2004 Mar 1. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 14726649 Review.
-
Ran GTPase in nuclear envelope formation and cancer metastasis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;773:323-51. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-8032-8_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24563355 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Blockade of Small GTPase RAN Inhibits Glioblastoma Cell Viability.Front Oncol. 2019 Jan 8;8:662. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00662. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30671385 Free PMC article.
-
Ran is a potential therapeutic target for cancer cells with molecular changes associated with activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 and Ras/MEK/ERK pathways.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 15;18(2):380-91. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2035. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22090358 Free PMC article.
-
Rho GTPases and their roles in cancer metabolism.Trends Mol Med. 2013 Feb;19(2):74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2012.10.011. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Trends Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23219172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ran GTPase and Its Importance in Cellular Signaling and Malignant Phenotype.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 4;24(4):3065. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043065. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Nuclear Cap-Binding Complex, a multitasking binding partner of RNA polymerase II transcripts.J Biochem. 2023 Dec 20;175(1):9-15. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvad081. J Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37830942 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stewart M. (2007) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 195–208 - PubMed
-
- Görlich D., Kraft R., Kostka S., Vogel F., Hartmann E., Laskey R. A., Mattaj I. W., Izaurralde E. (1996) Cell 87, 21–32 - PubMed
-
- Izaurralde E., Lewis J., McGuigan C., Jankowska M., Darzynkiewicz E., Mattaj I. W. (1994) Cell 78, 657–668 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

