Evolutionary conservation of the signaling proteins upstream of cyclic AMP-dependent kinase and protein kinase C in gastropod mollusks
- PMID: 20029183
- PMCID: PMC2855279
- DOI: 10.1159/000258666
Evolutionary conservation of the signaling proteins upstream of cyclic AMP-dependent kinase and protein kinase C in gastropod mollusks
Abstract
The protein kinase C (PKC) and the cAMP-dependent kinase (protein kinase A; PKA) pathways are known to play important roles in behavioral plasticity and learning in the nervous systems of a wide variety of species across phyla. We briefly review the members of the PKC and PKA family and focus on the evolution of the immediate upstream activators of PKC and PKA i.e., phospholipase C (PLC) and adenylyl cyclase (AC), and their conservation in gastropod mollusks, taking advantage of the recent assembly of the Aplysiacalifornica and Lottia gigantea genomes. The diversity of PLC and AC family members present in mollusks suggests a multitude of possible mechanisms to activate PKA and PKC; we briefly discuss the relevance of these pathways to the known physiological activation of these kinases in Aplysia neurons during plasticity and learning. These multiple mechanisms of activation provide the gastropod nervous system with tremendous flexibility for implementing neuromodulatory responses to both neuronal activity and extracellular signals.
Copyright 2009 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

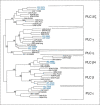
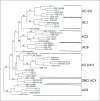
Similar articles
-
Parathyroid Hormone Activates Phospholipase C (PLC)-Independent Protein Kinase C Signaling Pathway via Protein Kinase A (PKA)-Dependent Mechanism: A New Defined Signaling Route Would Induce Alternative Consideration to Previous Conceptions.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Apr 20;23:1896-1906. doi: 10.12659/msm.903699. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28424452 Free PMC article.
-
mAChRs in the grasshopper brain mediate excitation by activation of the AC/PKA and the PLC second-messenger pathways.J Neurophysiol. 2002 Feb;87(2):876-88. doi: 10.1152/jn.00312.2001. J Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 11826053
-
Physiological crosstalk between the AC/PKA and PLC/PKC pathways modulates melatonin-mediated, monochromatic-light-induced proliferation of T-lymphocytes in chickens.Cell Tissue Res. 2017 Sep;369(3):555-565. doi: 10.1007/s00441-017-2644-6. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Cell Tissue Res. 2017. PMID: 28660299
-
Alteration of second messengers during acute cerebral ischemia - adenylate cyclase, cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, and cyclic AMP response element binding protein.Prog Neurobiol. 2001 Oct;65(2):173-207. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(01)00002-8. Prog Neurobiol. 2001. PMID: 11403878 Review.
-
Phosphoinositide signaling in unicellular eukaryotes.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2007;33(3):141-56. doi: 10.1080/10408410701415927. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17653984 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of genes related to learning and memory in the brain transcriptome of the mollusc, Hermissenda crassicornis.Learn Mem. 2015 Nov 16;22(12):617-21. doi: 10.1101/lm.038158.115. Print 2015 Dec. Learn Mem. 2015. PMID: 26572652 Free PMC article.
-
A Closely Associated Phospholipase C Regulates Cation Channel Function through Phosphoinositide Hydrolysis.J Neurosci. 2018 Aug 29;38(35):7622-7634. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0586-18.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 23. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30037836 Free PMC article.
-
The rates of protein synthesis and degradation account for the differential response of neurons to spaced and massed training protocols.PLoS Comput Biol. 2011 Dec;7(12):e1002324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002324. Epub 2011 Dec 29. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 22219722 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Characterization of a Vesicular Glutamate Transporter in an Interneuron That Makes Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Connections in a Molluscan Neural Circuit.J Neurosci. 2015 Jun 17;35(24):9137-49. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0180-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26085636 Free PMC article.
-
Novel calpain families and novel mechanisms for calpain regulation in Aplysia.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 20;12(10):e0186646. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186646. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29053733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrams TW, Yovell Y, Onyike CU, Cohen JE, Jarrard HE. Analysis of sequence-dependent interactions between transient calcium and transmitter stimuli in activating adenylyl cyclase in Aplysia: possible contribution to CS-US sequence requirement during conditioning. Learn Mem. 1998;4:496–509. - PubMed
-
- Antonov I, Antonova I, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD. Activity-dependent presynaptic facilitation and Hebbian LTP are both required and interact during classical conditioning in Aplysia. Neuron. 2003;37:135–147. - PubMed
-
- Azhderian EM, Kaczmarek LK. Cyclic AMP regulates processing of neuropeptide precursor in bag cell neurons of Aplysia. J Mol Neurosci. 1990;2:61–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

