An improved SUMmOn-based methodology for the identification of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like protein conjugation sites identifies novel ubiquitin-like protein chain linkages
- PMID: 20029837
- PMCID: PMC3374337
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.200900648
An improved SUMmOn-based methodology for the identification of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like protein conjugation sites identifies novel ubiquitin-like protein chain linkages
Abstract
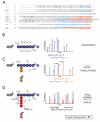
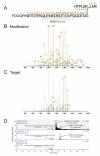
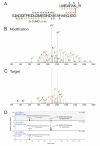
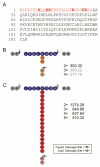
Ubiquitin (Ub) and the ubiquitin-like proteins (Ubls) comprise a remarkable assortment of polypeptides that are covalently conjugated to target proteins (or other biomolecules) to modulate their intracellular localization, half-life, and/or activity. Identification of Ub/Ubl conjugation sites on a protein of interest can thus be extremely important for understanding how it is regulated. While MS has become a powerful tool for the study of many classes of PTMs, the identification of Ub/Ubl conjugation sites presents a number of unique challenges. Here, we present an improved Ub/Ubl conjugation site identification strategy, utilizing SUMmOn analysis and an additional protease (lysyl endopeptidase C), as a complement to standard approaches. As compared with standard trypsin proteolysis-database search protocols alone, the addition of SUMmOn analysis can (i) identify Ubl conjugation sites that are not detected by standard database searching methods, (ii) better preserve Ub/Ubl conjugate identity, and (iii) increase the number of identifications of Ub/Ubl modifications in lysine-rich protein regions. Using this methodology, we characterize for the first time a number of novel Ubl linkages and conjugation sites, including alternative yeast (K54) and mammalian small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) chain (SUMO-2 K42, SUMO-3 K41) assemblies, as well as previously unreported NEDD8 chain (K27, K33, and K54) topologies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Using mass spectrometry to identify ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like protein conjugation sites.Proteomics. 2009 Feb;9(4):922-34. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200800666. Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19180541 Review.
-
An improved workflow for identifying ubiquitin/ubiquitin-like protein conjugation sites from tandem mass spectra.Proteomics. 2013 Sep;13(17):2579-84. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201300151. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23828837
-
Structure and evolution of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-related domains.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;832:15-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-474-2_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22350875
-
Binding surface mapping of intra- and interdomain interactions among hHR23B, ubiquitin, and polyubiquitin binding site 2 of S5a.J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 19;278(38):36621-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304628200. Epub 2003 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12832454
-
Probing ubiquitin and SUMO conjugation and deconjugation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2018 Apr 17;46(2):423-436. doi: 10.1042/BST20170086. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018. PMID: 29588386 Review.
Cited by
-
Recognition and cleavage of related to ubiquitin 1 (Rub1) and Rub1-ubiquitin chains by components of the ubiquitin-proteasome system.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Dec;11(12):1595-611. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.022467. Epub 2012 Oct 26. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 23105008 Free PMC article.
-
Global analysis of SUMO chain function reveals multiple roles in chromatin regulation.J Cell Biol. 2013 Apr 1;201(1):145-63. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201210019. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23547032 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamics and mechanism of SUMO chain deconjugation by SUMO-specific proteases.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 25;286(12):10238-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.205153. Epub 2011 Jan 19. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21247896 Free PMC article.
-
Neddylation, an Emerging Mechanism Regulating Cardiac Development and Function.Front Physiol. 2020 Dec 17;11:612927. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.612927. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33391028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein neddylation and its role in health and diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Apr 5;9(1):85. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01800-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38575611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schwartz DC, Hochstrasser M. A superfamily of protein tags: ubiquitin, SUMO and related modifiers. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28:321–328. - PubMed
-
- Kerscher O, Felberbaum R, Hochstrasser M. Modification of proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:159–180. - PubMed
-
- Ciechanover A, Iwai K. The ubiquitin system: from basic mechanisms to the patient bed. IUBMB Life. 2004;56:193–201. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

