The effects of size, shape, and surface functional group of gold nanostructures on their adsorption and internalization by cells
- PMID: 20029850
- PMCID: PMC3011366
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.200901622
The effects of size, shape, and surface functional group of gold nanostructures on their adsorption and internalization by cells
Abstract
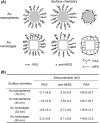
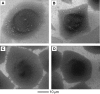
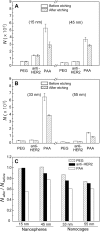
In this study, we examined the effects of size, shape, and surface chemistry of gold nanostructures on their uptake (including both adsorption and internalization) by SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells. We used both spherical and cubic Au nanostructures (nanospheres and nanocages, respectively) of two different sizes, and their surface was modified with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), antibody anti-HER2, or poly(allyamine hydrochloride) (PAA). Our results showed that the size of the Au nanostructures influenced their uptake by the cells in a similar way regardless of the surface chemistry, while the shape dependency could vary depending on the surface functional group. In addition, the cells preferred to take up the Au nanostructures covered by different surface groups in the following order: PAA>> anti-HER2> PEG. The fraction of Au nanostructures attached to the cell surface was also dependent on the aforementioned parameters.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

