Decoding of lipoprotein-receptor interactions: properties of ligand binding modules governing interactions with apolipoprotein E
- PMID: 20030366
- PMCID: PMC2821871
- DOI: 10.1021/bi9017208
Decoding of lipoprotein-receptor interactions: properties of ligand binding modules governing interactions with apolipoprotein E
Abstract
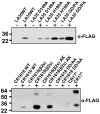
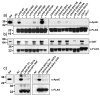
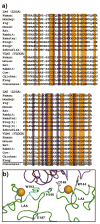
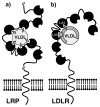
Clusters of complement-type ligand binding repeats in the LDL receptor family are thought to mediate the interactions between these receptors and their various ligands. Apolipoprotein E, a key ligand for cholesterol homeostasis, has been shown to interact with LDLR, LRP, and VLDLR, through these clusters. LDLR and VLDLR each contain a single ligand binding repeat cluster, whereas LRP contains three large clusters of ligand binding repeats, each with ligand binding functions. We show that within sLRP3 the three-repeat subcluster CR16-18 recapitulated ligand binding to the isolated receptor binding portion of ApoE (residues 130-149). Binding experiments with LA3-5 of LDLR and CR16-18 showed that a conserved W25/D30 pair appears to be critical for high-affinity binding to ApoE(130-149). The triple repeat LA3-5 showed the expected interaction with ApoE(1-191).DMPC, but surprisingly CR16-18 did not interact with this form of ApoE. To understand these differences in ApoE binding affinity, we introduced mutations of conserved residues from LA5 into CR18 and produced a CR16-18 variant capable of binding ApoE(1-191).DMPC. This change cannot fully be accounted for by the interaction with the proposed ApoE receptor binding region; therefore, we speculate that LA5 is recognizing a distinct epitope on ApoE that may only exist in the lipid-bound form. The combination of avidity effects with this distinct recognition process likely governs the ApoE-LDL receptor interaction.
Figures
References
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986;232:34–47. - PubMed
-
- Hui DY, Innerarity TL, Mahley RW. Defective hepatic lipoprotein receptor binding of B-very low density lipoproteins from type 111 hyperlipoproteinemic patients: importance of apolipoprotein E. J Biol Chem. 1984:259. - PubMed
-
- Hussain MM, Maxfield FR, Más-Oliva J, Tabas I, Ji ZS, Innerarity TL, Mahley RW. Clearance of chylomicron remnants by the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:13936–13940. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

