T-cell activation profiles in different granulomatous interstitial lung diseases--a role for CD8+CD28(null) cells?
- PMID: 20030671
- PMCID: PMC2857949
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04076.x
T-cell activation profiles in different granulomatous interstitial lung diseases--a role for CD8+CD28(null) cells?
Abstract
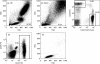
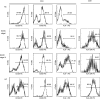
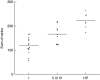
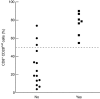
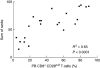
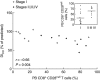
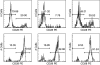
Lymphocytes play a crucial role in lung inflammation. Different interstitial lung diseases may show distinct lymphocyte activation profiles. The aim of this study was to examine the expression of a variety of activation markers on T lymphocyte subsets from blood and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of patients with different granulomatous interstitial lung diseases and healthy controls. Bronchoalveolar lavage cells and blood cells from 23 sarcoidosis patients, seven patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis and 24 healthy controls were analysed. Lymphocyte activation status was determined by flow cytometry. Lymphocytes were stained with antibodies against CD3, CD4, CD8, CD25, CD28, CD69, very late antigen-1 (VLA)-1, VLA-4 and human leucocyte antigen D-related (HLA-DR). In general, CD28, CD69 and VLA-1 expression on BALF CD4+ lymphocytes and HLA-DR expression on BALF CD8+ lymphocytes was different in patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis and sarcoidosis patients with parenchymal involvement. This BALF lymphocyte phenotype correlated with carbon monoxide diffusing lung capacity (Dlco) values across interstitial lung diseases (ILD) (r2 = 0.48, P = 0.0002). In sarcoidosis patients, CD8+CD28(null) blood lymphocytes correlated with lower Dlco values (r = -0.66, P = 0.004), chronic BALF lymphocyte activation phenotype (r2 = 0.65, P < 0.0001), radiographic staging (stage I versus stage II and higher, P = 0.006) and with the need for corticosteroid treatment (P = 0.001). Higher expression of CD69, VLA-1 and HLA-DR and lower expression of CD28 on BALF lymphocytes suggests prolonged stimulation and chronic lymphocyte activation in patients with ILD. In sarcoidosis, blood CD8+CD28(null) cells might be a new biomarker for disease severity but needs further investigation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrin α E β 7 (CD103) expression in bronchoalveolar lymphocytes of patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis.Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2015 Feb;88(2):167-73. doi: 10.1007/s00420-014-0947-4. Epub 2014 May 30. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2015. PMID: 24874839
-
Is the different T helper cell activity in sarcoidosis and extrinsic allergic alveolitis also reflected by the cellular bronchoalveolar lavage fluid profile?Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1997 Mar;14(1):31-8. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1997. PMID: 9186987
-
Density of phenotypic markers on BAL T-lymphocytes in hypersensitivity pneumonitis, pulmonary sarcoidosis and bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia.Eur Respir J. 1993 Apr;6(4):477-82. Eur Respir J. 1993. PMID: 8491296
-
[Deep lung--cellular reaction to HIV].Rev Port Pneumol. 2007 Mar-Apr;13(2):175-212. Rev Port Pneumol. 2007. PMID: 17492233 Review. Portuguese.
-
Dendritic Cell Trafficking and Function in Rare Lung Diseases.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017 Oct;57(4):393-402. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0051PS. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28586276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lymphocyte senescence in COPD is associated with loss of glucocorticoid receptor expression by pro-inflammatory/cytotoxic lymphocytes.Respir Res. 2015 Jan 9;16(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12931-014-0161-7. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 25573300 Free PMC article.
-
Management of hypersensivity pneumonitis.Clin Transl Allergy. 2013 Feb 4;3(1):5. doi: 10.1186/2045-7022-3-5. Clin Transl Allergy. 2013. PMID: 23374544 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of IL-17RC associated with ocular sarcoidosis.J Transl Med. 2014 May 31;12:152. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-152. J Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 24885153 Free PMC article.
-
Activated CD8(+) T cells and NKT cells in BAL fluid improve diagnostic accuracy in sarcoidosis.Lung. 2014 Feb;192(1):133-40. doi: 10.1007/s00408-013-9527-8. Epub 2013 Nov 10. Lung. 2014. PMID: 24213536
-
CD4/CD8 T-cell ratio in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid as a marker of sarcoidosis severity: a retrospective study.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 May 9;25(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03428-5. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40346566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henke CE, Henke G, Elveback LR, Beard CM, Ballard DJ, Kurland LT. The epidemiology of sarcoidosis in Rochester, Minnesota: a population-based study of incidence and survival. Am J Epidemiol. 1986;123:840–5. - PubMed
-
- Hillerdal G, Nou E, Osterman K, Schmekel B. Sarcoidosis: epidemiology and prognosis. A 15-year European study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984;130:29–32. - PubMed
-
- Newman LS, Rose CS, Maier LA. Sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1224–34. - PubMed
-
- Crystal RG, Bitterman PB, Rennard SI, Hance AJ, Keogh BA. Interstitial lung diseases of unknown cause. Disorders characterized by chronic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract. N Engl J Med. 1984;310:235–44. - PubMed
-
- Bourke SJ, Dalphin JC, Boyd G, McSharry C, Baldwin CI, Calvert JE. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: current concepts. Eur Respir J Suppl. 2001;32:81s–92s. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

