Normal kidney size and its influencing factors - a 64-slice MDCT study of 1.040 asymptomatic patients
- PMID: 20030823
- PMCID: PMC2813848
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2490-9-19
Normal kidney size and its influencing factors - a 64-slice MDCT study of 1.040 asymptomatic patients
Abstract
Background: Normal ultrasound values for pole-to-pole kidney length (LPP) are well established for children, but very little is known about normal kidney size and its influencing factors in adults. The objectives of this study were thus to establish normal CT values for kidney dimensions from a group of unselected patients, identify potential influencing factors, and to estimate their significance.
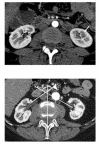
Methods: In multiphase thin-slice MDCTs of 2.068 kidneys in 1.040 adults, the kidney length pole to pole (LPP), parenchymal (PW) and cortical width (CW), position and rotation status of the kidneys, number of renal arteries, pyelon width and possible influencing factors that can be visualized, were recorded from a volume data set. For length measurements, axes were adjusted individually in double oblique planes using a 3D-software. Analyses of distribution, T-tests, ANOVA, correlation and multivariate regression analyses were performed.
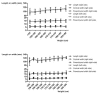
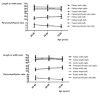
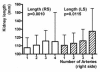
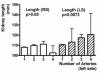
Results: LPP was 108.5 +/- 12.2 mm for the right, and 111.3 +/- 12.6 mm for the left kidney (p < 0.0001 each). PW on the right side was 15.4 +/- 2.8 mm, slightly less than 15.9 +/- 2.7 mm on the left side (p < 0.0001), the CW was the same (6.6 +/- 1.9 mm). The most significant independent predictors for LPP, CW, and PW were body size, BMI, age, and gender (p < 0.001 each). In men, the LPP increases up to the fifth decade of life (p < 0.01). It is also influenced by the position of the kidneys, stenoses and number of renal arteries (SRA/NRA), infarctions suffered, parapelvic cysts, and absence of the contralateral kidney; CW is influenced by age, position, parapelvic cysts, NRA and SRA, and the PW is influenced in addition by rotation status (p < 0.05 each). Depending on the most important factors, gender-specific normal values were indicated for these dimensions, the length and width in cross section, width of the renal pelvis, and parenchyma-renal pyelon ratio.
Conclusions: Due to the complex influences on kidney size, assessment should be made individually. The most important influencing factors are BMI, height, gender, age, position of the kidneys, stenoses and number of renal arteries.
Figures


References
-
- Hederström E, Forsberg L. Kidney size in children assessed by ultrasonography and urography. Acta Radiol Diagn. 1985;26:85–91. - PubMed
-
- Edell SL, Kurtz AB, Rifkin MD. In: Atlas of ultrasound measurements. Goldberg BB, Kutz AB, editor. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers; 1990. Normal renal ultrasund measurements; p. 146.
-
- Emamian SA, Nielsen MB, Pedersen JF, Ytte L. Kidney dimensions at sonography: correlation with age, sex, and habitus in 665 adult volunteers. AJR. 1993;160:83–86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

