The Arabidopsis BET bromodomain factor GTE4 is involved in maintenance of the mitotic cell cycle during plant development
- PMID: 20032077
- PMCID: PMC2832235
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.150631
The Arabidopsis BET bromodomain factor GTE4 is involved in maintenance of the mitotic cell cycle during plant development
Abstract
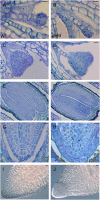
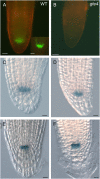
Bromodomain and Extra Terminal domain (BET) proteins are characterized by the presence of two types of domains, the bromodomain and the extra terminal domain. They bind to acetylated lysines present on histone tails and control gene transcription. They are also well known to play an important role in cell cycle regulation. In Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), there are 12 BET genes; however, only two of them, IMBIBITION INDUCIBLE1 and GENERAL TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR GROUP E6 (GTE6), were functionally analyzed. We characterized GTE4 and show that gte4 mutant plants have some characteristic features of cell cycle mutants. Their size is reduced, and they have jagged leaves and a reduced number of cells in most organs. Moreover, cell size is considerably increased in the root, and, interestingly, the root quiescent center identity seems to be partially lost. Cell cycle analyses revealed that there is a delay in activation of the cell cycle during germination and a premature arrest of cell proliferation, with a switch from mitosis to endocycling, leading to a statistically significant increase in ploidy levels in the differentiated organs of gte4 plants. Our results point to a role of GTE4 in cell cycle regulation and specifically in the maintenance of the mitotic cell cycle.
Figures



Comment in
-
The Arabidopsis BET bromodomain factor GTE4 regulates the mitotic cell cycle.Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Jun;5(6):677-80. doi: 10.4161/psb.5.6.11571. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20495359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aida K, Beis D, Heidstra R, Willemsen V, Blilou I, Galinha C, Nussaume L, Noh YS, Amasino R, Scheres B. (2004) The PLETHORA genes mediate patterning of the Arabidopsis root stem cell niche. Cell 119: 109–120 - PubMed
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al. (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Bode AM, Dong Z. (2005) Inducible covalent posttranslational modification of histone H3. Sci STKE 26: re4. - PubMed
-
- Boudolf V, Vlieghe K, Beemster GT, Magyar Z, Torres Acosta JA, Maes S, Van Der Schueren E, Inzé D, De Veylder L. (2004) The plant-specific cyclin-dependent kinase CDKB1;1 and transcription factor E2Fa-DPa control the balance of mitotically dividing and endoreduplicating cells in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16: 2683–2692 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

