Expression and function of CXCL12/CXCR4 in rat urinary bladder with cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis
- PMID: 20032115
- PMCID: PMC2838600
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00628.2009
Expression and function of CXCL12/CXCR4 in rat urinary bladder with cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis
Abstract
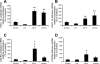
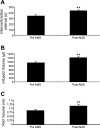
Chemokines, otherwise known as chemotactic cytokines, are proinflammatory mediators of the immune response and have been implicated in altered sensory processing, hyperalgesia, and central sensitization following tissue injury or inflammation. To address the role of CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling in normal micturition and inflammation-induced bladder hyperreflexia, bladder inflammation in adult female Wistar rats (175-250 g) was induced by injecting cyclophosphamide (CYP) intraperitoneally at acute (150 mg/kg; 4 h), intermediate (150 mg/kg; 48 h), and chronic (75 mg/kg; every 3rd day for 10 days) time points. CXCL12, and its receptor, CXCR4, were examined in the whole urinary bladder of control and CYP-treated rats using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR), and immunostaining techniques. ELISAs, qRT-PCR, and immunostaining experiments revealed a significant (P < or = 0.01) increase in CXCL12 and CXCR4 expression in the whole urinary bladder, and particularly in the urothelium, with CYP treatment. The functional role of CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling in micturition was evaluated using conscious cystometry with continuous instillation of saline and CXCR4 receptor antagonist (AMD-3100; 5 microM) administration in control and CYP (48 h)-treated rats. Receptor blockade of CXCR4 using AMD-3100 increased bladder capacity in control (no CYP) rats and reduced CYP-induced bladder hyperexcitability as demonstrated by significant (P < or = 0.01) increases in intercontraction interval, bladder capacity, and void volume. These results suggest a role for CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling in both normal micturition and with bladder hyperreflexia following bladder inflammation.
Figures
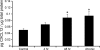






References
-
- Apodaca G, Balestreire E, Birder LA. The uroepithelial-associated sensory web. Kidney Int 72: 1057–1064, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Arms L, Vizzard MA. Distribution and function of chemokine/receptor systems in cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced cystitis in rats (Abstract). Program No. 372.19. 2009 Neuroscience Meeting Planner Chicago, IL: Society for Neuroscience, 2009. Online
-
- Azab AK, Runnels JM, Pitsillides C, Moreau AS, Azab F, Leleu X, Jia X, Wright R, Ospina B, Carlson AL, Alt C, Burwick N, Roccaro AM, Ngo HT, Farag M, Melhem MR, Sacco A, Munshi NC, Hideshima T, Rollins BJ, Anderson KC, Kung AL, Lin CP, Ghobrial IM. CXCR4 inhibitor AMD3100 disrupts the interaction of multiple myeloma cells with the bone marrow microenvironment and enhances their sensitivity to therapy. Blood 113: 4341–4351, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balabanian K, Lagane B, Infantino S, Chow KY, Harriague J, Moepps B, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Thelen M, Bachelerie F. The chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12 binds to and signals through the orphan receptor RDC1 in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 280: 35760–35766, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

