Angiotensin II AT2 receptor regulates ureteric bud morphogenesis
- PMID: 20032120
- PMCID: PMC2838588
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00147.2009
Angiotensin II AT2 receptor regulates ureteric bud morphogenesis
Abstract
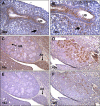
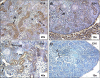
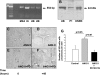
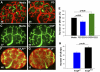
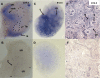
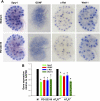
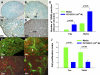
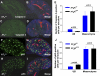
ANG II AT2 receptor (AT2R)-deficient mice exhibit abnormal ureteric bud (UB) budding, increased incidence of double ureters, and vesicoureteral reflux. However, the role of the AT2R during UB morphogenesis and the mechanisms by which aberrant AT2R signaling disrupts renal collecting system development have not been fully defined. In this study, we mapped the expression of the AT2R during mouse metanephric development, examined the impact of disrupted AT2R signaling on UB branching, cell proliferation, and survival, and investigated the cross talk of the AT2R with the glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF)/c-Ret/Wnt11 signaling pathway. Embryonic mouse kidneys express AT2R in the branching UB and the mesenchyme. Treatment of embryonic day 12.5 (E12.5) metanephroi with the AT2R antagonist PD123319 or genetic inactivation of the AT2R in mice inhibits UB branching, decreasing the number of UB tips compared with control (34 +/- 1.0 vs. 43 +/- 0.6, P < 0.01; 36 +/- 1.8 vs. 48 +/- 1.3, P < 0.01, respectively). In contrast, treatment of metanephroi with the AT2R agonist CGP42112 increases the number of UB tips compared with control (48 +/- 1.8 vs. 39 +/- 12.3, P < 0.05). Using real-time quantitative RT-PCR and whole mount in situ hybridization, we demonstrate that PD123319 downregulates the expression of GDNF, c-Ret, Wnt11, and Spry1 mRNA levels in E12.5 metanephroi grown ex vivo. AT(2)R blockade or genetic inactivation of AT2R stimulates apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of the UB cells in vivo. We conclude that AT2R performs essential functions during UB branching morphogenesis via control of the GDNF/c-Ret/Wnt11 signaling pathway, UB cell proliferation, and survival.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Downregulation of Spry-1, an inhibitor of GDNF/Ret, causes angiotensin II-induced ureteric bud branching.Kidney Int. 2008 Nov;74(10):1287-93. doi: 10.1038/ki.2008.378. Epub 2008 Jul 23. Kidney Int. 2008. PMID: 18650792 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II-induced activation of c-Ret signaling is critical in ureteric bud branching morphogenesis.Mech Dev. 2010 Jan-Feb;127(1-2):21-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2009.11.004. Epub 2009 Dec 2. Mech Dev. 2010. PMID: 19961928 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt11 and Ret/Gdnf pathways cooperate in regulating ureteric branching during metanephric kidney development.Development. 2003 Jul;130(14):3175-85. doi: 10.1242/dev.00520. Development. 2003. PMID: 12783789
-
A new role for the renin-angiotensin system in the development of the ureteric bud and renal collecting system.Keio J Med. 2008 Dec;57(4):184-9. doi: 10.2302/kjm.57.184. Keio J Med. 2008. PMID: 19110530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GDNF/Ret signaling and the development of the kidney.Bioessays. 2006 Feb;28(2):117-27. doi: 10.1002/bies.20357. Bioessays. 2006. PMID: 16435290 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of PGP 9.5, NGFR, TGFβ1, FGFR1, MMP-2, AT2R2, SHH, and TUNEL in Primary Obstructive Megaureter Tissue.J Histochem Cytochem. 2022 Feb;70(2):139-149. doi: 10.1369/00221554211063515. Epub 2021 Dec 17. J Histochem Cytochem. 2022. PMID: 34915763 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II stimulates in vitro branching morphogenesis of the isolated ureteric bud.Mech Dev. 2011 Sep-Dec;128(7-10):359-67. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2011.07.002. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Mech Dev. 2011. PMID: 21820050 Free PMC article.
-
The ureteric bud epithelium: morphogenesis and roles in metanephric kidney patterning.Mol Reprod Dev. 2015 Mar;82(3):151-66. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22462. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Mol Reprod Dev. 2015. PMID: 25783232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The origin and role of the renal stroma.Development. 2021 Oct 1;148(19):dev199886. doi: 10.1242/dev.199886. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Development. 2021. PMID: 34553766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Angiotensin AT2 Receptor: From a Binding Site to a Novel Therapeutic Target.Pharmacol Rev. 2022 Oct;74(4):1051-1135. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000281. Pharmacol Rev. 2022. PMID: 36180112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Awqati Q, Goldberg MR. Architectural patterns in branching morphogenesis in the kidney. Kidney Int 54: 832–1842, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Barasch J, Pressler L, Connor J, Malik A. A ureteric bud cell line induces nephrogenesis in two steps by distinct signals. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 271: F50–F61, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Basson MA, Watson-Johnson J, Shakya R, Akbulut S, Hyink D, Costantini FD, Wilson PD, Mason IJ, Licht JD. Branching morphogenesis of the ureteric epithelium during kidney development is coordinated by the opposing functions of GDNF and Sprouty1. Dev Biol 299: 466–77, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Berry C, Touyz R, Dominiczak AF, Webb RC, Johns DG. Angiotensin receptors: signaling, vascular pathophysiology, and interactions with ceramide. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281: H2337–H2365, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Brechler V, Jones PW, Levens NR, de Gasparo M, Bottari SP. Agonistic and antagonistic properties of angiotensin analogs at the AT2 receptor in PC12W cells. Regul Pept 44: 207–213, 1993 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

