Regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 enhanceosome formation by apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 in hepatic acute phase response
- PMID: 20032196
- PMCID: PMC2817606
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0319
Regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 enhanceosome formation by apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 in hepatic acute phase response
Abstract
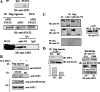
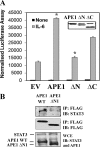
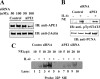
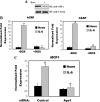
The signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) is a latent IL-6 inducible transcription factor that mediates hepatic and vascular inflammation. In this study, we make the novel observation that STAT3 forms an inducible complex with the apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1)/redox effector factor-1 (APE1/Ref-1), an essential multifunctional protein in DNA base excision repair, and studied the role of APE1/Ref-1 in STAT3 function. Using a transfection-coimmunoprecipitation assay, we observed that APE1 selectively binds the NH(2)-terminal acetylation domain of STAT3. Ectopic expression of APE1 potentiated inducible STAT3 reporter activity, whereas knockdown of APE1 resulted in reduced IL-6-inducible acute-phase reactant protein expression (C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression. The mechanism for APE1 requirement in IL-6 signaling was indicated by reduced STAT3 DNA binding activity observed in response to small interfering RNA-mediated APE1 silencing. Consistent with these in vitro studies, we also observed that lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of acute-phase reactant protein expression is significantly abrogated in APE1 heterozygous mice compared with wild-type mice. IL-6 induces both STAT3 and APE1 to bind the suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 and gamma-fibrionogen promoters in their native chromatin environment. Moreover, we observed that APE1 knockdown destabilized formation of the STAT3-inducible enhanceosome on the endogenous gamma-fibrionogen promoter. Taken together, our study indicates that IL-6 induces a novel STAT3-APE1 complex, whose interaction is required for stable chromatin association in the IL-6-induced hepatic acute phase response.
Figures


References
-
- Levy DE, Darnell Jr JE 2002 Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:651–662 - PubMed
-
- Darnell Jr JE, Kerr IM, Stark GR 1994 Jak-STAT pathways and transcritptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 264:1415–1421 - PubMed
-
- Darnell Jr JE 1997 STATs and gene regulation. Science 277:1630–1635 - PubMed
-
- Schindler C, Darnell Jr JE 1995 Transcriptional response to polypeptide ligands: the JAK-STAT pathway. Annu Rev Biochem 64:621–651 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

