Identification of a variety of Staphylococcus species by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry
- PMID: 20032251
- PMCID: PMC2832446
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00413-09
Identification of a variety of Staphylococcus species by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry
Abstract
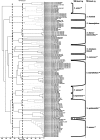
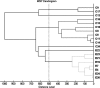
Whole-cell fingerprinting by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) in combination with a dedicated bioinformatic software tool (MALDI Biotyper 2.0) was used to identify 152 staphylococcal strains corresponding to 22 staphylococcal species. Spectra of the 152 isolates, previously identified at the species level using a sodA gene-based oligonucleotide array, were analyzed against the main spectra of 3,030 microorganisms. A total of 151 strains out of 152 (99.3%) were correctly identified at the species level; only one strain was identified at the genus level. The MALDI-TOF MS method revealed different clonal lineages of Staphylococcus epidermidis that were of either human or environmental origin, which suggests that the MALDI-TOF MS method could be useful in the profiling of staphylococcal strains. The topology of the dendrogram generated by the MALDI Biotyper 2.0 software from the spectra of 120 Staphylococcus reference strains (representing 36 species) was in general agreement with that inferred from the 16S rRNA gene-based analysis. Our findings indicate that the MALDI-TOF MS technology, associated with a broad-spectrum reference database, is an effective tool for the swift and reliable identification of Staphylococci.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implementation of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry in Routine Clinical Laboratories Improves Identification of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci and Reveals the Pathogenic Role of Staphylococcus lugdunensis.J Clin Microbiol. 2015 Jul;53(7):2030-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00177-15. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Clin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25878345 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Identification of Staphylococcus Species Isolated from Food Samples by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Apr 28;29(4):548-557. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1901.01046. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30939633
-
Optimization of the score cutoff value for routine identification of Staphylococcus species by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015 Dec;83(4):349-54. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26423657
-
Challenging the problem of clostridial identification with matrix-assisted laser desorption and ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS).Anaerobe. 2008 Oct;14(4):242-9. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2008.06.002. Epub 2008 Jun 24. Anaerobe. 2008. PMID: 18621134
-
Accurate differentiation of novel Staphylococcus argenteus from Staphylococcus aureus using MALDI-TOF MS.Future Microbiol. 2018 Jul;13:997-1006. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2018-0015. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Future Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29952240
Cited by
-
Implementation of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry in Routine Clinical Laboratories Improves Identification of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci and Reveals the Pathogenic Role of Staphylococcus lugdunensis.J Clin Microbiol. 2015 Jul;53(7):2030-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00177-15. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Clin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25878345 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of clinical Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates among other alpha and nonhemolytic streptococci by use of the Vitek MS matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry system.J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Jun;51(6):1861-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.03069-12. Epub 2013 Apr 10. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23576536 Free PMC article.
-
Marinobacter salarius sp. nov. and Marinobacter similis sp. nov., isolated from sea water.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 8;9(9):e106514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106514. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25198502 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of MALDI-TOF MS and VITEK 2 in bacteria identification.J Thorac Dis. 2014 May;6(5):534-8. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.02.18. J Thorac Dis. 2014. PMID: 24822115 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and cluster analysis of Streptococcus pyogenes by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e47152. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047152. Epub 2012 Nov 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23144803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergonier, D., R. de Cremoux, R. Rupp, G. Lagriffoul, and X. Berthelot. 2003. Mastitis of dairy small ruminants. Vet. Res. 34:689-716. - PubMed
-
- Carbonnelle, E., J. L. Beretti, S. Cottyn, G. Quesne, P. Berche, X. Nassif, and A. Ferroni. 2007. Rapid identification of staphylococci isolated in clinical microbiology laboratories by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 45:2156-2161. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choi, S. H., J. H. Woo, J. Y. Jeong, N. J. Kim, M. N. Kim, Y. S. Kim, and J. Ryu. 2006. Clinical significance of Staphylococcus saprophyticus identified on blood culture in a tertiary care hospital. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 56:337-339. - PubMed
-
- Claydon, M. A., S. N. Davey, V. Edwards-Jones, and D. B. Gordon. 1996. The rapid identification of intact microorganisms using mass spectrometry. Nat. Biotechnol. 14:1584-1586. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

