Hypoglycemia aggravates critical illness-induced neurocognitive dysfunction
- PMID: 20032274
- PMCID: PMC2827523
- DOI: 10.2337/dc09-1740
Hypoglycemia aggravates critical illness-induced neurocognitive dysfunction
Abstract
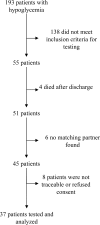
OBJECTIVE Tight glycemic control (TGC) in critically ill patients is associated with an increased risk of hypoglycemia. Whether those short episodes of hypoglycemia are associated with adverse morbidity and mortality is a matter of discussion. Using a case-control study design, we investigated whether hypoglycemia under TGC causes permanent neurocognitive dysfunction in patients surviving critical illness. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS From our patient data management system, we identified adult survivors treated for >72 h in our surgical intensive care unit (ICU) between 2004 and 2007 (n = 4,635) without a history of neurocognitive dysfunction or structural brain abnormalities who experienced at least one episode of hypoglycemia during treatment (hypo group) (n = 37). For each hypo group patient, one patient stringently matched for demographic- and disease-related data were identified as a control subject. We performed a battery of neuropsychological tests investigating five areas of cognitive functioning in both groups at least 1 year after ICU discharge. Test results were compared with data from healthy control subjects and between groups. RESULTS Critical illness caused neurocognitive dysfunction in all tested domains in both groups. The dysfunction was aggravated in hypo group patients in one domain, namely that of visuospatial skills (P < 0.01). Besides hypoglycemia, both hyperglycemia (r = -0.322; P = 0.005) and fluctuations of blood glucose (r = -0.309; P = 0.008) were associated with worse test results in this domain. CONCLUSIONS Hypoglycemia was found to aggravate critical illness-induced neurocognitive dysfunction to a limited, but significant, extent; however, an impact of hyperglycemia and fluctuations of blood glucose on neurocognitive function cannot be excluded.
Figures
References
-
- Van den Berghe G, Wouters P, Weekers F, Verwaest C, Bruyninckx F, Schetz M, Vlasselaers D, Ferdinande P, Lauwers P, Bouillon R: Intensive insulin therapy in the critically ill patients. N Engl J Med 2001;345:1359–1367 - PubMed
-
- Vanhorebeek I, Langouche L, Van den Berghe G: Tight blood glucose control with insulin in the ICU: facts and controversies. Chest 2007;132:268–278 - PubMed
-
- NICE-SUGAR Study Investigators. Finfer S, Chittock DR, Su SY, Blair D, Foster D, Dhingra V, Bellomo R, Cook D, Dodek P, Henderson WR, Hebert PC, Heritier S, Heyland DK, McArthur C, McDonald E, Mitchell I, Myburgh JA, Norton R, Potter J, Robinson BG, Ronco JJ: Intensive versus conventional glucose control in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med 2009;360:1283–1297 - PubMed
-
- Brunkhorst FM, Engel C, Bloos F, Meier-Hellmann A, Ragaller M, Weiler N, Moerer O, Gruendling M, Oppert M, Grond S, Olthoff D, Jaschinski U, John S, Rossaint R, Welte T, Schaefer M, Kern P, Kuhnt E, Kiehntopf M, Hartog C, Natanson C, Loeffler M, Reinhart K: the German Competence Network Sepsis (SepNet). Intensive insulin therapy and pentastarch resuscitation in severe sepsis. N Engl J Med 2008;358:125–139 - PubMed