Alzheimer Abeta peptide induces chromosome mis-segregation and aneuploidy, including trisomy 21: requirement for tau and APP
- PMID: 20032300
- PMCID: PMC2820417
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-10-0850
Alzheimer Abeta peptide induces chromosome mis-segregation and aneuploidy, including trisomy 21: requirement for tau and APP
Abstract
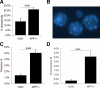
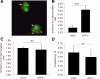
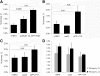
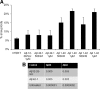
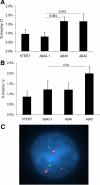
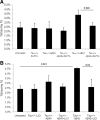
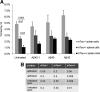
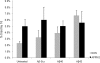
Both sporadic and familial Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients exhibit increased chromosome aneuploidy, particularly trisomy 21, in neurons and other cells. Significantly, trisomy 21/Down syndrome patients develop early onset AD pathology. We investigated the mechanism underlying mosaic chromosome aneuploidy in AD and report that FAD mutations in the Alzheimer Amyloid Precursor Protein gene, APP, induce chromosome mis-segregation and aneuploidy in transgenic mice and in transfected cells. Furthermore, adding synthetic Abeta peptide, the pathogenic product of APP, to cultured cells causes rapid and robust chromosome mis-segregation leading to aneuploid, including trisomy 21, daughters, which is prevented by LiCl addition or Ca(2+) chelation and is replicated in tau KO cells, implicating GSK-3beta, calpain, and Tau-dependent microtubule transport in the aneugenic activity of Abeta. Furthermore, APP KO cells are resistant to the aneugenic activity of Abeta, as they have been shown previously to be resistant to Abeta-induced tau phosphorylation and cell toxicity. These results indicate that Abeta-induced microtubule dysfunction leads to aneuploid neurons and may thereby contribute to the pathogenesis of AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitotic spindle defects and chromosome mis-segregation induced by LDL/cholesterol-implications for Niemann-Pick C1, Alzheimer's disease, and atherosclerosis.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 12;8(4):e60718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060718. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593294 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Trisomy 21 Mosaicism in Sporadic and Familial Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(1):7-17. doi: 10.2174/156720501301151207100616. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26651340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble Conformers of Aβ and Tau Alter Selective Proteins Governing Axonal Transport.J Neurosci. 2016 Sep 14;36(37):9647-58. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1899-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27629715 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting increased levels of APP in Down syndrome: Posiphen-mediated reductions in APP and its products reverse endosomal phenotypes in the Ts65Dn mouse model.Alzheimers Dement. 2021 Feb;17(2):271-292. doi: 10.1002/alz.12185. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. PMID: 32975365 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta Clearance and p-Tau Accumulation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Rodent Models: Is Fractalkine a Systemic Biomarker for AD?Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(4):403-12. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151116125714. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26567742 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitotic spindle defects and chromosome mis-segregation induced by LDL/cholesterol-implications for Niemann-Pick C1, Alzheimer's disease, and atherosclerosis.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 12;8(4):e60718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060718. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593294 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Trisomy 21: Phenotypic Variability in People with Down Syndrome Explained by Further Chromosome Mis-segregation and Mosaic Aneuploidy.J Down Syndr Chromosom Abnorm. 2016;2(1):109. doi: 10.4172/2472-1115.1000109. Epub 2016 Mar 31. J Down Syndr Chromosom Abnorm. 2016. PMID: 29516054 Free PMC article.
-
A Unified Hypothesis of Early- and Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;47(1):33-47. doi: 10.3233/JAD-143210. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 26402752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental Expression of 4-Repeat-Tau Induces Neuronal Aneuploidy in Drosophila Tauopathy Models.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 23;7:40764. doi: 10.1038/srep40764. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28112163 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in MAPT give rise to aneuploidy in animal models of tauopathy.Neurogenetics. 2014 Mar;15(1):31-40. doi: 10.1007/s10048-013-0380-y. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Neurogenetics. 2014. PMID: 24218087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Busciglio J., Yankner B. A. Apoptosis and increased generation of reactive oxygen species in Down's syndrome neurons in vitro. Nature. 1997;378:776–779. - PubMed
-
- Chromy B. A., et al. Self-assembly of Abeta(1-42) into globular neurotoxins. Biochemistry. 2003;42:12749–12760. - PubMed
-
- Chui D. H., et al. Transgenic mice with Alzheimer presenilin 1 mutations show accelerated neurodegeneration without amyloid plaque formation. Nat. Med. 1999;5:560–564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

