Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent regulation of platelet-activating factor receptor as a route for gram-positive bacterial translocation across epithelia
- PMID: 20032301
- PMCID: PMC2820419
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-07-0573
Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent regulation of platelet-activating factor receptor as a route for gram-positive bacterial translocation across epithelia
Abstract
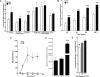
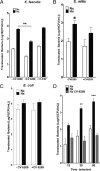
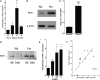
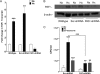
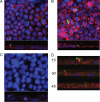
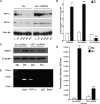
Mucosal surfaces, such as the lung and intestine, are lined by a monolayer of epithelia that provides tissue barrier and transport function. It is recently appreciated that a common feature of inflammatory processes within the mucosa is hypoxia (so-called inflammatory hypoxia). Given the strong association between bacterial translocation and mucosal inflammatory disease, we hypothesized that intestinal epithelial hypoxia influences bacterial translocation. Initial studies revealed that exposure of cultured intestinal epithelia to hypoxia (pO(2), 20 torr; 24-48 h) resulted in a increase of up to 40-fold in the translocation of some strains of Gram-positive bacteria, independently of epithelial barrier function. A screen of relevant pathway inhibitors identified a prominent role for the platelet-activating factor receptor (PAFr) in hypoxia-associated bacterial translocation, wherein pharmacologic antagonists of PAFr blocked bacterial translocation by as much as 80 +/- 6%. Extensions of these studies revealed that hypoxia prominently induces PAFr through a hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-dependent mechanism. Indeed, HIF and PAFr loss of function studies (short hairpin RNA) revealed that apically expressed PAFr is central to the induction of translocation for the Gram-positive bacteria Enterococcus faecalis. Together, these findings reveal that some strains of Gram-positive bacteria exploit HIF-regulated PAFr as a means for translocation through intestinal epithelial cells.
Figures
References
-
- Barbier M., Oliver A., Rao J., Hanna S. L., Goldberg J. B., Alberti S. Novel phosphorylcholine-containing protein of Pseudomonas aeruginosa chronic infection isolates interacts with airway epithelial cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2008;197:465–473. - PubMed
-
- Caplan M. S., Hedlund E., Adler L., Lickerman M., Hsueh W. The platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist WEB 2170 prevents neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis in rats. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1997;24:296–301. - PubMed
-
- Caplan M. S., Simon D., Jilling T. The role of PAF, TLR, and the inflammatory response in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2005;14:145–151. - PubMed
-
- Claud E. C., Li D., Xiao Y., Caplan M. S., Jilling T. Platelet-activating factor regulates chloride transport in colonic epithelial cell monolayers. Pediatr. Res. 2002;52:155–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

