The cell surface protein gene ecm33+ is a target of the two transcription factors Atf1 and Mbx1 and negatively regulates Pmk1 MAPK cell integrity signaling in fission yeast
- PMID: 20032302
- PMCID: PMC2820430
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-09-0810
The cell surface protein gene ecm33+ is a target of the two transcription factors Atf1 and Mbx1 and negatively regulates Pmk1 MAPK cell integrity signaling in fission yeast
Abstract
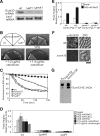
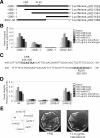
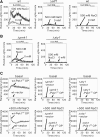
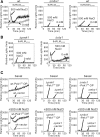
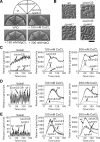
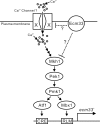
The highly conserved fission yeast Pmk1 MAPK pathway plays a key role in cell integrity by regulating Atf1, which belongs to the ATF/cAMP-responsive element-binding (CREB) protein family. We identified and characterized ecm33(+), which encodes a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface protein as a transcriptional target of Pmk1 and Atf1. We demonstrated that the gene expression of Ecm33 is regulated by two transcription factors Atf1 and a MADS-box-type transcription factor Mbx1. We identified a putative ATF/CREB-binding site and an RLM1-binding site in the ecm33(+) promoter region and monitored the transcriptional activity of Atf1 or Mbx1 in living cells using a destabilized luciferase reporter gene fused to three tandem repeats of the CRE and six tandem repeats of the Rlm1-binding sequence, respectively. These reporter genes reflect the activation of the Pmk1 pathway by various stimuli, thereby enabling the real-time monitoring of the Pmk1 cell integrity pathway. Notably, the Deltaecm33 cells displayed hyperactivation of the Pmk1 signaling together with hypersensitivity to Ca(2+) and an abnormal morphology, which were almost abolished by simultaneous deletion of the components of the Rho2/Pck2/Pmk1 pathway. Our results suggest that Ecm33 is involved in the negative feedback regulation of Pmk1 cell integrity signaling and is linked to cellular Ca(2+) signaling.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Cell surface protein Ecm33 is involved in negative feedback regulation of MAP kinase signalling and development of the in vivo real-time monitoring of MAP kinase signalling].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2011;131(8):1195-200. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.131.1195. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2011. PMID: 21804323 Review. Japanese.
-
Atf1 is a target of the mitogen-activated protein kinase Pmk1 and regulates cell integrity in fission yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Dec;18(12):4794-802. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-03-0282. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17881729 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the fission yeast cell integrity MAPK pathway in response to glucose limitation.BMC Microbiol. 2013 Feb 11;13:34. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-34. BMC Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23398982 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the role of the signal- and Sty1 kinase-dependent phosphorylation of the stress-responsive transcription factor Atf1 on gene activation.J Biol Chem. 2017 Aug 18;292(33):13635-13644. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.794339. Epub 2017 Jun 26. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28652406 Free PMC article.
-
Phospho-mimicking Atf1 mutants bypass the transcription activating function of the MAP kinase Sty1 of fission yeast.Curr Genet. 2018 Feb;64(1):97-102. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0730-7. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28799013 Review.
Cited by
-
The Fission Yeast Cell Integrity Pathway: A Functional Hub for Cell Survival upon Stress and Beyond.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Dec 30;8(1):32. doi: 10.3390/jof8010032. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35049972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of conidiation and antagonistic properties of the soil-borne plant beneficial fungus Trichoderma virens by a novel proline-, glycine-, tyrosine-rich protein and a GPI-anchored cell wall protein.Curr Genet. 2019 Aug;65(4):953-964. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00948-0. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30840111
-
Comparative proteomic analysis reveals the regulatory network of the veA gene during asexual and sexual spore development of Aspergillus cristatus.Biosci Rep. 2018 Jul 31;38(4):BSR20180067. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180067. Print 2018 Aug 31. Biosci Rep. 2018. Retraction in: Biosci Rep. 2021 Apr 30;41(4):BSR-20180067_RET. doi: 10.1042/BSR-20180067_RET. PMID: 29773679 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Biological significance of nuclear localization of mitogen-activated protein kinase Pmk1 in fission yeast.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 27;287(31):26038-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.345611. Epub 2012 Jun 8. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22685296 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Overview of Molecular Interactions and Enzymatic Activities in the Yeast Cell Walls.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 26;21(23):8996. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238996. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33256216 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agarwal A. K., Rogers P. D., Baerson S. R., Jacob M. R., Barker K. S., Cleary J. D., Walker L. A., Nagle D. G., Clark A. M. Genome-wide expression profiling of the response to polyene, pyrimidine, azole, and echinocandin antifungal agents in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:34998–35015. - PubMed
-
- Bahler J., Wu J. Q., Longtine M. S., Shah N. G., McKenzie A., III, Steever A. B., Wach A., Philippsen P., Pringle J. R. Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast. 1998;14:943–951. - PubMed
-
- Buck V., Ng S. S., Ruiz-Garcia A. B., Papadopoulou K., Bhatti S., Samuel J. M., Anderson M., Millar J. B., McInerny C. J. Fkh2p and Sep1p regulate mitotic gene transcription in fission yeast. J. Cell Sci. 2004;117:5623–5632. - PubMed
-
- Carnero E., Ribas J. C., Garcia B., Duran A., Sanchez Y. Schizosaccharomyces pombe ehs1p is involved in maintaining cell wall integrity and in calcium uptake. Mol. Gen. Genet. 2000;264:173–183. - PubMed
-
- De Groot P. W., Hellingwerf K. J., Klis F. M. Genome-wide identification of fungal GPI proteins. Yeast. 2003;20:781–796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

