The cell surface protein gene ecm33+ is a target of the two transcription factors Atf1 and Mbx1 and negatively regulates Pmk1 MAPK cell integrity signaling in fission yeast
- PMID: 20032302
- PMCID: PMC2820430
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-09-0810
The cell surface protein gene ecm33+ is a target of the two transcription factors Atf1 and Mbx1 and negatively regulates Pmk1 MAPK cell integrity signaling in fission yeast
Abstract
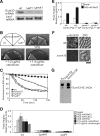
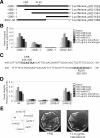
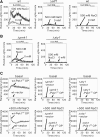
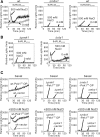
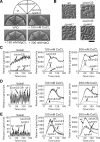
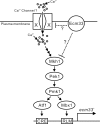
The highly conserved fission yeast Pmk1 MAPK pathway plays a key role in cell integrity by regulating Atf1, which belongs to the ATF/cAMP-responsive element-binding (CREB) protein family. We identified and characterized ecm33(+), which encodes a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface protein as a transcriptional target of Pmk1 and Atf1. We demonstrated that the gene expression of Ecm33 is regulated by two transcription factors Atf1 and a MADS-box-type transcription factor Mbx1. We identified a putative ATF/CREB-binding site and an RLM1-binding site in the ecm33(+) promoter region and monitored the transcriptional activity of Atf1 or Mbx1 in living cells using a destabilized luciferase reporter gene fused to three tandem repeats of the CRE and six tandem repeats of the Rlm1-binding sequence, respectively. These reporter genes reflect the activation of the Pmk1 pathway by various stimuli, thereby enabling the real-time monitoring of the Pmk1 cell integrity pathway. Notably, the Deltaecm33 cells displayed hyperactivation of the Pmk1 signaling together with hypersensitivity to Ca(2+) and an abnormal morphology, which were almost abolished by simultaneous deletion of the components of the Rho2/Pck2/Pmk1 pathway. Our results suggest that Ecm33 is involved in the negative feedback regulation of Pmk1 cell integrity signaling and is linked to cellular Ca(2+) signaling.
Figures


References
-
- Agarwal A. K., Rogers P. D., Baerson S. R., Jacob M. R., Barker K. S., Cleary J. D., Walker L. A., Nagle D. G., Clark A. M. Genome-wide expression profiling of the response to polyene, pyrimidine, azole, and echinocandin antifungal agents in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:34998–35015. - PubMed
-
- Bahler J., Wu J. Q., Longtine M. S., Shah N. G., McKenzie A., III, Steever A. B., Wach A., Philippsen P., Pringle J. R. Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast. 1998;14:943–951. - PubMed
-
- Buck V., Ng S. S., Ruiz-Garcia A. B., Papadopoulou K., Bhatti S., Samuel J. M., Anderson M., Millar J. B., McInerny C. J. Fkh2p and Sep1p regulate mitotic gene transcription in fission yeast. J. Cell Sci. 2004;117:5623–5632. - PubMed
-
- Carnero E., Ribas J. C., Garcia B., Duran A., Sanchez Y. Schizosaccharomyces pombe ehs1p is involved in maintaining cell wall integrity and in calcium uptake. Mol. Gen. Genet. 2000;264:173–183. - PubMed
-
- De Groot P. W., Hellingwerf K. J., Klis F. M. Genome-wide identification of fungal GPI proteins. Yeast. 2003;20:781–796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

