Vascular endothelial-cadherin stabilizes at cell-cell junctions by anchoring to circumferential actin bundles through alpha- and beta-catenins in cyclic AMP-Epac-Rap1 signal-activated endothelial cells
- PMID: 20032304
- PMCID: PMC2820423
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-07-0580
Vascular endothelial-cadherin stabilizes at cell-cell junctions by anchoring to circumferential actin bundles through alpha- and beta-catenins in cyclic AMP-Epac-Rap1 signal-activated endothelial cells
Abstract
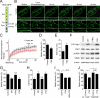
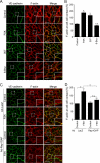
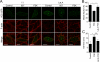
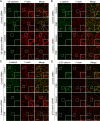
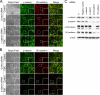
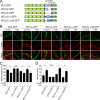
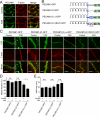
Vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin is a cell-cell adhesion molecule involved in endothelial barrier functions. Previously, we reported that cAMP-Epac-Rap1 signal enhances VE-cadherin-dependent cell adhesion. Here, we further scrutinized how cAMP-Epac-Rap1 pathway promotes stabilization of VE-cadherin at the cell-cell contacts. Forskolin induced circumferential actin bundling and accumulation of VE-cadherin fused with green fluorescence protein (VEC-GFP) on the bundled actin filaments. Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) analyses using VEC-GFP revealed that forskolin stabilizes VE-cadherin at cell-cell contacts. These effects of forskolin were mimicked by an activator for Epac but not by that for protein kinase A. Forskolin-induced both accumulation and stabilization of junctional VEC-GFP was impeded by latrunculin A. VE-cadherin, alpha-catenin, and beta-catenin were dispensable for forskolin-induced circumferential actin bundling, indicating that homophilic VE-cadherin association is not the trigger of actin bundling. Requirement of alpha- and beta-catenins for forskolin-induced stabilization of VE-cadherin on the actin bundles was confirmed by FRAP analyses using VEC-GFP mutants, supporting the classical model that alpha-catenin could potentially link the bundled actin to cadherin. Collectively, circumferential actin bundle formation and subsequent linkage between actin bundles and VE-cadherin through alpha- and beta-catenins are important for the stabilization of VE-cadherin at the cell-cell contacts in cAMP-Epac-Rap1 signal-activated cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cyclic AMP potentiates vascular endothelial cadherin-mediated cell-cell contact to enhance endothelial barrier function through an Epac-Rap1 signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jan;25(1):136-46. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.1.136-146.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15601837 Free PMC article.
-
[Signaling mechanism involved in regulation of endothelial cell-cell junctions].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010 Nov;130(11):1413-20. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.130.1413. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 21048397 Review. Japanese.
-
Epac1 regulates integrity of endothelial cell junctions through VE-cadherin.FEBS Lett. 2005 Sep 12;579(22):4966-72. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.07.080. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 16115630
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate rapidly increases endothelial barrier function independently of VE-cadherin but requires cell spreading and Rho kinase.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007 Oct;293(4):C1309-18. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00014.2007. Epub 2007 Aug 1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17670896
-
Dynamic Regulation of Vascular Permeability by Vascular Endothelial Cadherin-Mediated Endothelial Cell-Cell Junctions.J Nippon Med Sch. 2017;84(4):148-159. doi: 10.1272/jnms.84.148. J Nippon Med Sch. 2017. PMID: 28978894 Review.
Cited by
-
Vinculin strengthens the endothelial barrier during vascular development.Vasc Biol. 2023 Jan 27;5(1):e220012. doi: 10.1530/VB-22-0012. Print 2023 Jan 1. Vasc Biol. 2023. PMID: 36260739 Free PMC article.
-
γ-Actin plays a key role in endothelial cell motility and neovessel maintenance.Vasc Cell. 2015 Feb 6;7:2. doi: 10.1186/s13221-014-0027-2. eCollection 2015. Vasc Cell. 2015. PMID: 25705373 Free PMC article.
-
EphrinA/EphA signal facilitates insulin-like growth factor-I-induced myogenic differentiation through suppression of the Ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 cascade in myoblast cell lines.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Sep;22(18):3508-19. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-03-0183. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21795402 Free PMC article.
-
Exchange protein directly activated by cAMP plays a critical role in regulation of vascular fibrinolysis.Life Sci. 2019 Mar 15;221:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.02.014. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30738042 Free PMC article.
-
KRIT1: A Traffic Warden at the Busy Crossroads Between Redox Signaling and the Pathogenesis of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Mar;38(7-9):496-528. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0263. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 36047808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adamson R. H., Ly J. C., Sarai R. K., Lenz J. F., Altangerel A., Drenckhahn D., Curry F. E. Epac/Rap1 pathway regulates microvascular hyperpermeability induced by PAF in rat mesentery. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008;294:H1188–H1196. - PubMed
-
- Andriopoulou P., Navarro P., Zanetti A., Lampugnani M. G., Dejana E. Histamine induces tyrosine phosphorylation of endothelial cell-to-cell adherens junctions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999;19:2286–2297. - PubMed
-
- Augustin H. G., Young K. G., Thurston G., Alitalo K. Control of vascular morphogenesis and homeostasis through the angiopoietin-Tie system. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009;10:165–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

