Interactions between copper-binding sites determine the redox status and conformation of the regulatory N-terminal domain of ATP7B
- PMID: 20032459
- PMCID: PMC2825428
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.074633
Interactions between copper-binding sites determine the redox status and conformation of the regulatory N-terminal domain of ATP7B
Abstract
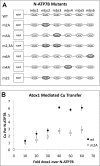
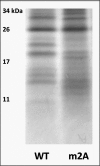
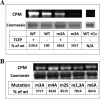
Copper-transporting ATPase ATP7B is essential for human copper homeostasis and normal liver function. ATP7B has six N-terminal metal-binding domains (MBDs) that sense cytosolic copper levels and regulate ATP7B. The mechanism of copper sensing and signal integration from multiple MBDs is poorly understood. We show that MBDs communicate and that this communication determines the oxidation state and conformation of the entire N-terminal domain of ATP7B (N-ATP7B). Mutations of copper-coordinating Cys to Ala in any MBD (2, 3, 4, or 6) change the N-ATP7B conformation and have distinct functional consequences. Mutating MBD2 or MBD3 causes Cys oxidation in other MBDs and loss of copper binding. In contrast, mutation of MBD4 and MBD6 does not alter the redox status and function of other sites. Our results suggest that MBD2 and MBD3 work together to regulate access to other metal-binding sites, whereas MBD4 and MBD6 receive copper independently, downstream of MBD2 and MBD3. Unlike Ala substitutions, the Cys-to-Ser mutation in MBD2 preserves the conformation and reduced state of N-ATP7B, suggesting that hydrogen bonds contribute to interdomain communications. Tight coupling between MBDs suggests a mechanism by which small changes in individual sites (induced by copper binding or mutation) result in stabilization of distinct conformations of the entire N-ATP7B and altered exposure of sites for interactions with regulatory proteins.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

