T cells and dendritic cells in glomerular disease: the new glomerulotubular feedback loop
- PMID: 20032960
- PMCID: PMC3039448
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2009.489
T cells and dendritic cells in glomerular disease: the new glomerulotubular feedback loop
Abstract
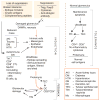
A newly described glomerulotubular feedback loop may explain the relationship between glomerular damage, epitope spreading, tubulointerstitial nephritis, proteinuria as a progression factor, and the importance of the local milieu in kidney damage. It also opens the horizons for exciting innovative approaches to therapy of both acute and chronic kidney diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Rocklin R, Lewis E, David J. In-vitro evidence for cellular hypersensitivity to glomerular-basement membrane antigens in human glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med. 1970;283:497–501. - PubMed
-
- Dixon FJ. What are sensitized cells doing in glomerulonephritis? N Engl J Med. 1970;283:536–537. - PubMed
-
- Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Lan HY, Atkins R. Macrophages in immune renal injury. In: Neilson EG, Couser WG, editors. Immunologic Renal Diseases. Lippincott-Raven; Philadelphia: 1997. pp. 575–592.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

